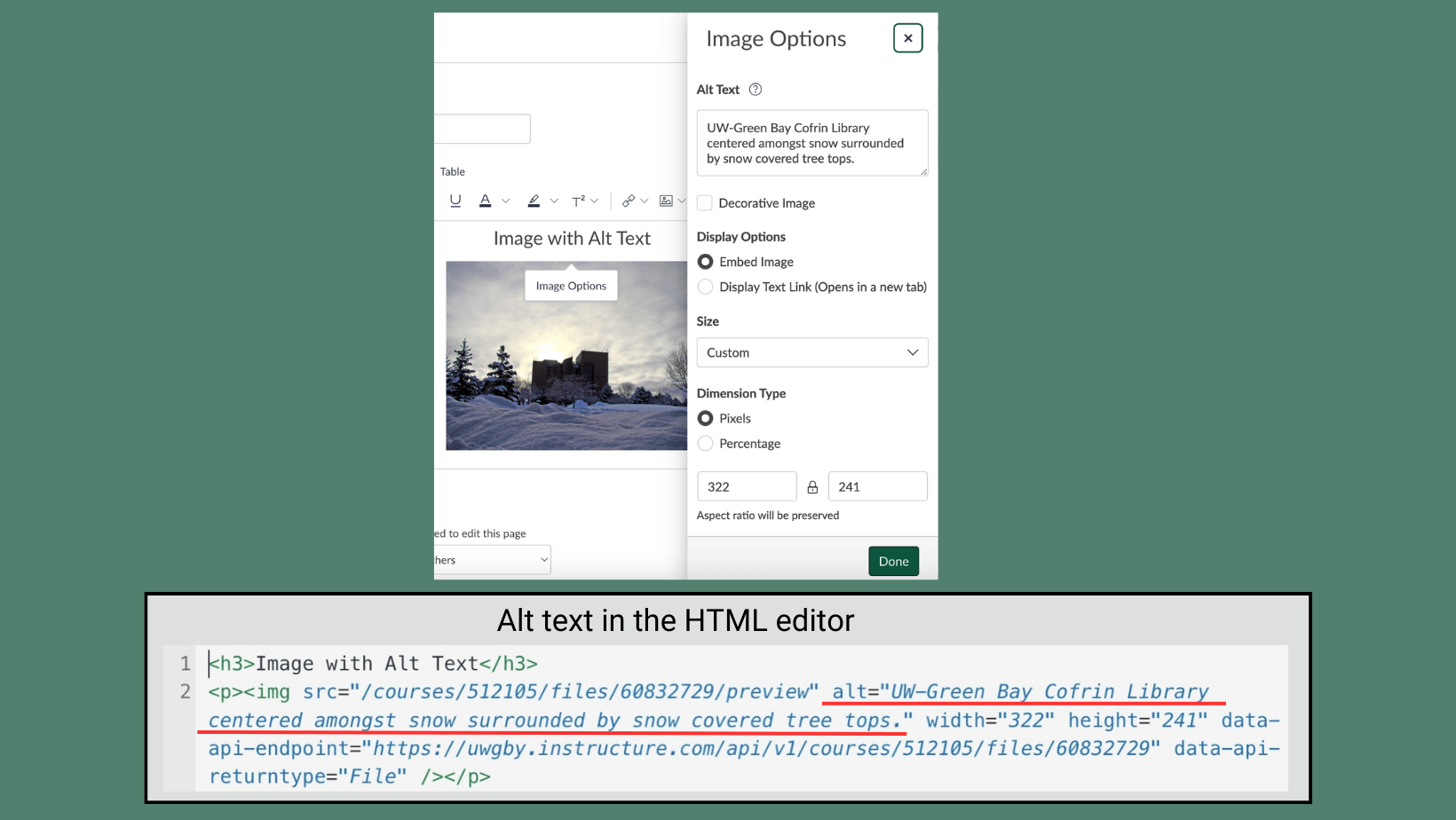
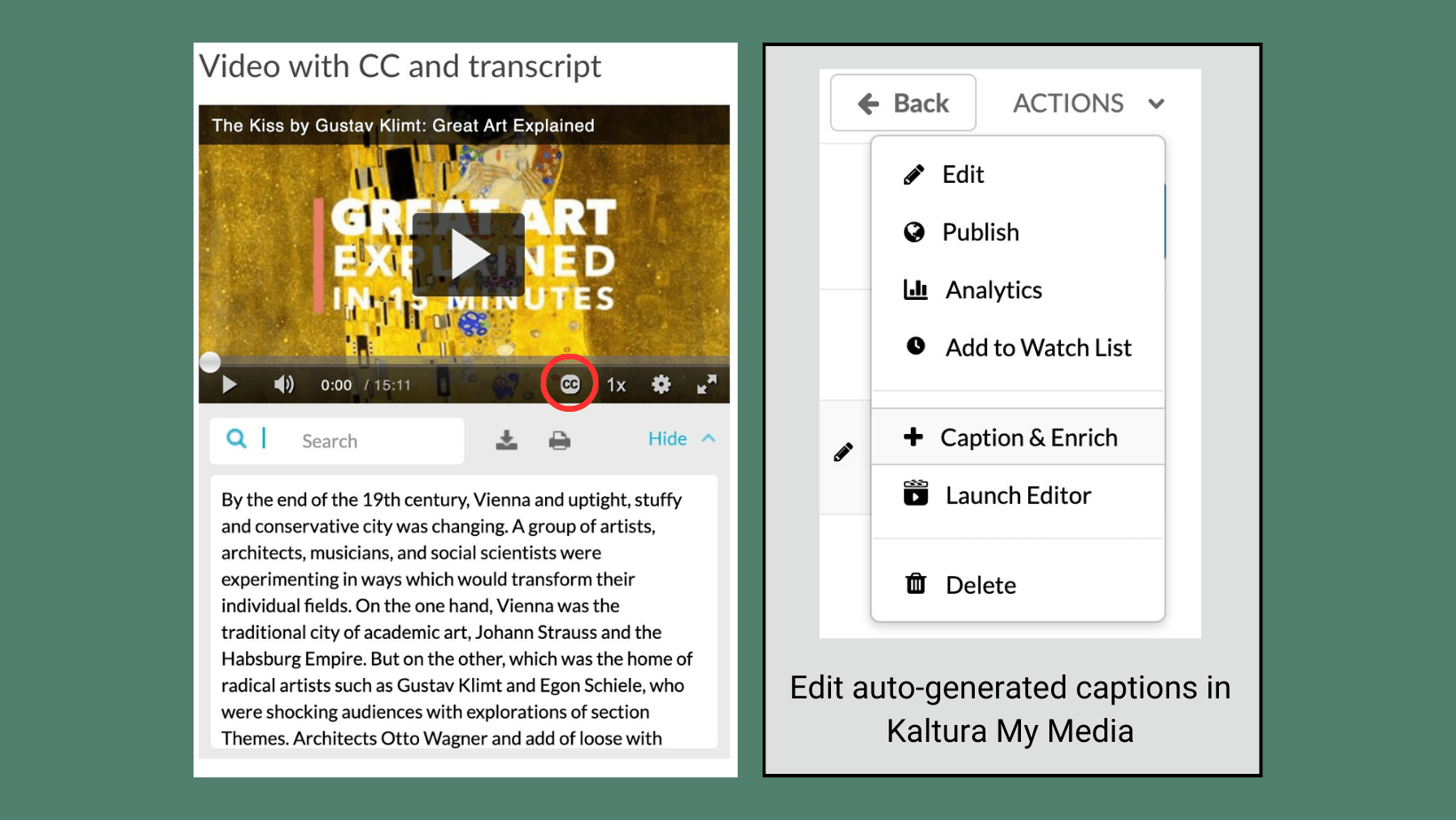
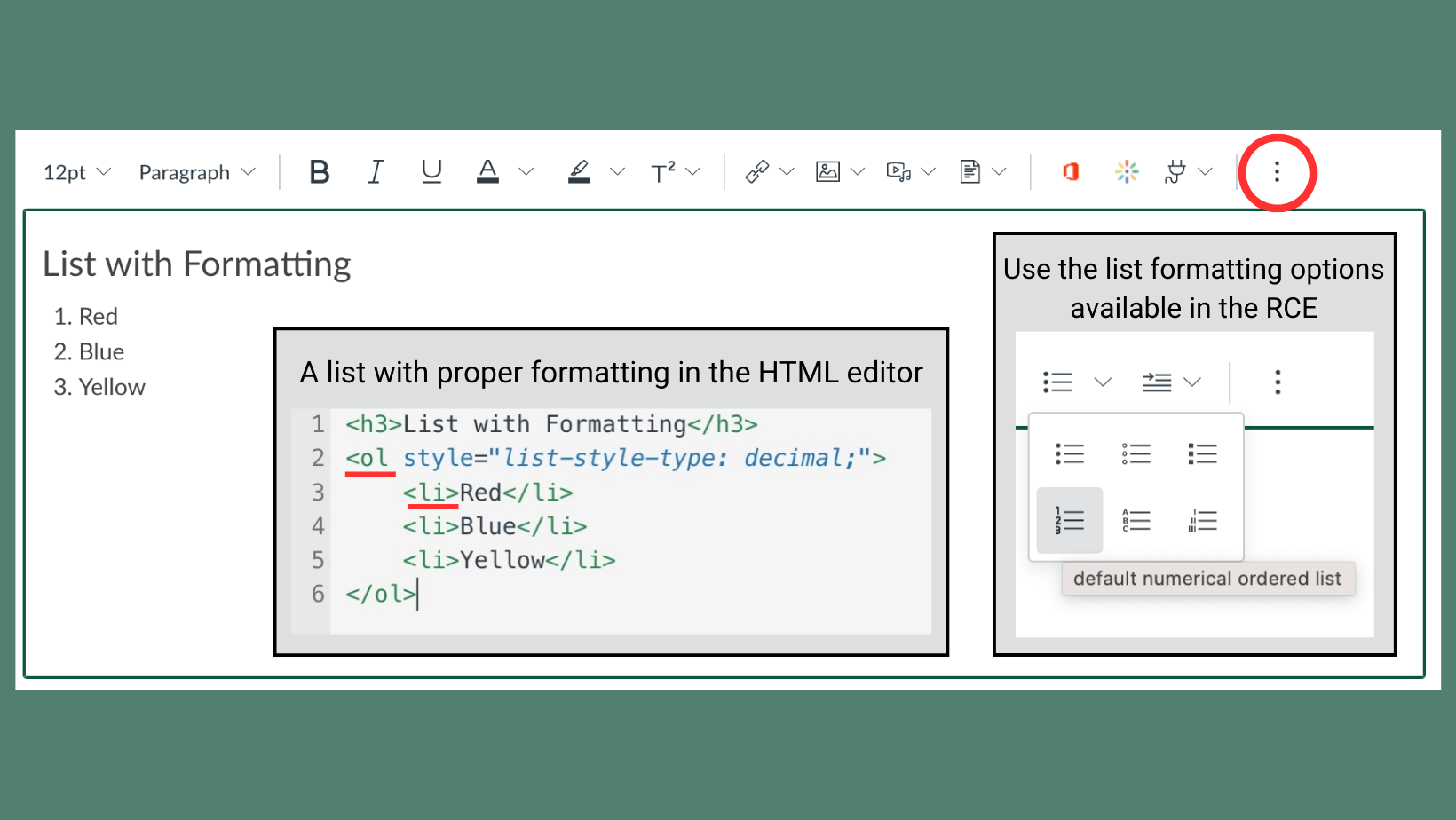
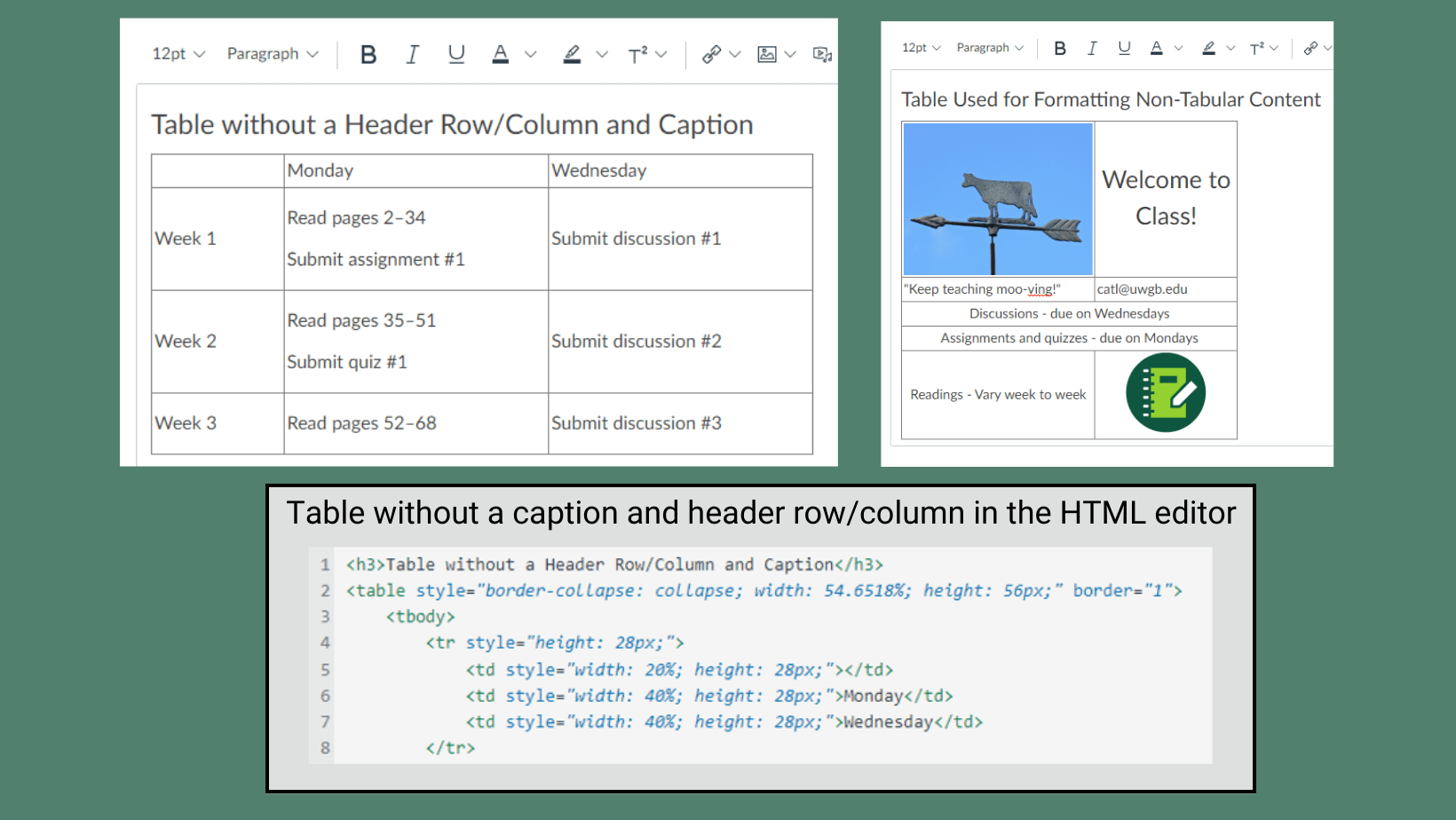
The University of Wisconsin – Green Bay uses Canvas as its Learning Management System (LMS). When instructors participate in professional development opportunities offered by the Center for the Advancement of Teaching and Learning (CATL), they often encounter information about creating a Canvas Sandbox course. But what exactly is a sandbox course? This blog post will define what a sandbox course is, what the differences are between a sandbox course and an instructional course, and some different use cases for sandbox courses that will help save you time in the long run.
What is a sandbox course?
A sandbox course is an empty Canvas course shell that can be used for a wide variety of purposes. These courses are not linked to the UWGB course registrar the way instructional courses are. Therefore, Sandbox courses can be used as a testing field or playground within the Canvas environment. Sandbox courses can be used by instructors as a tool to engage with Canvas content and teaching materials with other faculty or staff.
How is a sandbox course different from an instructional course?
- Sandbox course: A sandbox course can be manually created at any time. These courses are not linked to a specific term within Canvas and do not have term start or end dates. Sandbox courses are not linked to the Registrar or SIS, so they do not have automatic enrollments and do not have any students.
- Instructional course: An instructional course is created 75 days before the start date of the course as it is listed in the Schedule of Classes. These courses are linked to the UWGB student information system (SIS) which automatically enrolls students. This same system also automatically updates student enrollments as students add and drop courses at the beginning of a term to keep your course enrollments up to date. Both the instructor and students within a Canvas instructional course are added with SIS system sync. Therefore, the only Teachers within an instructional course are those listed as an instructor of record by the Registrar’s Office and only students who officially enroll in a course are added to an instructional course shell.
What are the limitations and benefits of a sandbox course?
Sandbox courses do not have the option to add someone to the course as a “Student.” This is a setting enforced by the University of Wisconsin System. Instructors can, however, utilize the “Student View” option in Canvas to view content in their Sandbox courses as a student would see it. To do so, any modules and content of interest must be published.
Canvas sandbox courses also allow for multiple individuals to have the role of “Teacher” at the same time. As sandbox courses are not linked to the SIS system, these roles can be granted by anyone within the course who has the role of “Teacher”. This allows for multiple instructors to contribute collaboratively to learning materials and activities to a course, or to allow instructors to share content with each other without worry that students will have access to those resources.
How can you utilize a sandbox course (instructors and staff)?
- Sharing course content with other instructors or staff members while being mindful of FERPA. This is the safest way to share course content between instructors.
- Preemptively building out your course content prior to the creation of your Instructional Canvas courses (these show up 75 days before the listed course start date). Content built in a sandbox course prior to the creation of an instructional course can be moved into the live instructional course using the Canvas Course Import tool.
- Make “live” revisions to course content during an active teaching term without impacting the instructional course your students are engaging in. The best way to do this is to build a sandbox course and then copy the course content from your instructional course into the sandbox course. Then you can make reflective edits to that content in the sandbox course without impacting the activities that students have engaged with.
- Collaborative course design and course building with a co-instructor or designers.
- Creation of departmental or program trainings for instructors, staff, graduate students, and/or student employees. If you would like to create a course shell for training and development purposes and need to add users with the “Student” role, please reach out to dle@uwgb.edu and a Canvas admin can copy your sandbox into a course shell that supports the Student role.
- Testing and experimenting to build new activities or assessments using different integrations (LTIs) such as PlayPosit and Hypothesis that are available within in the UWGB Canvas instance.
How do I create a sandbox course?
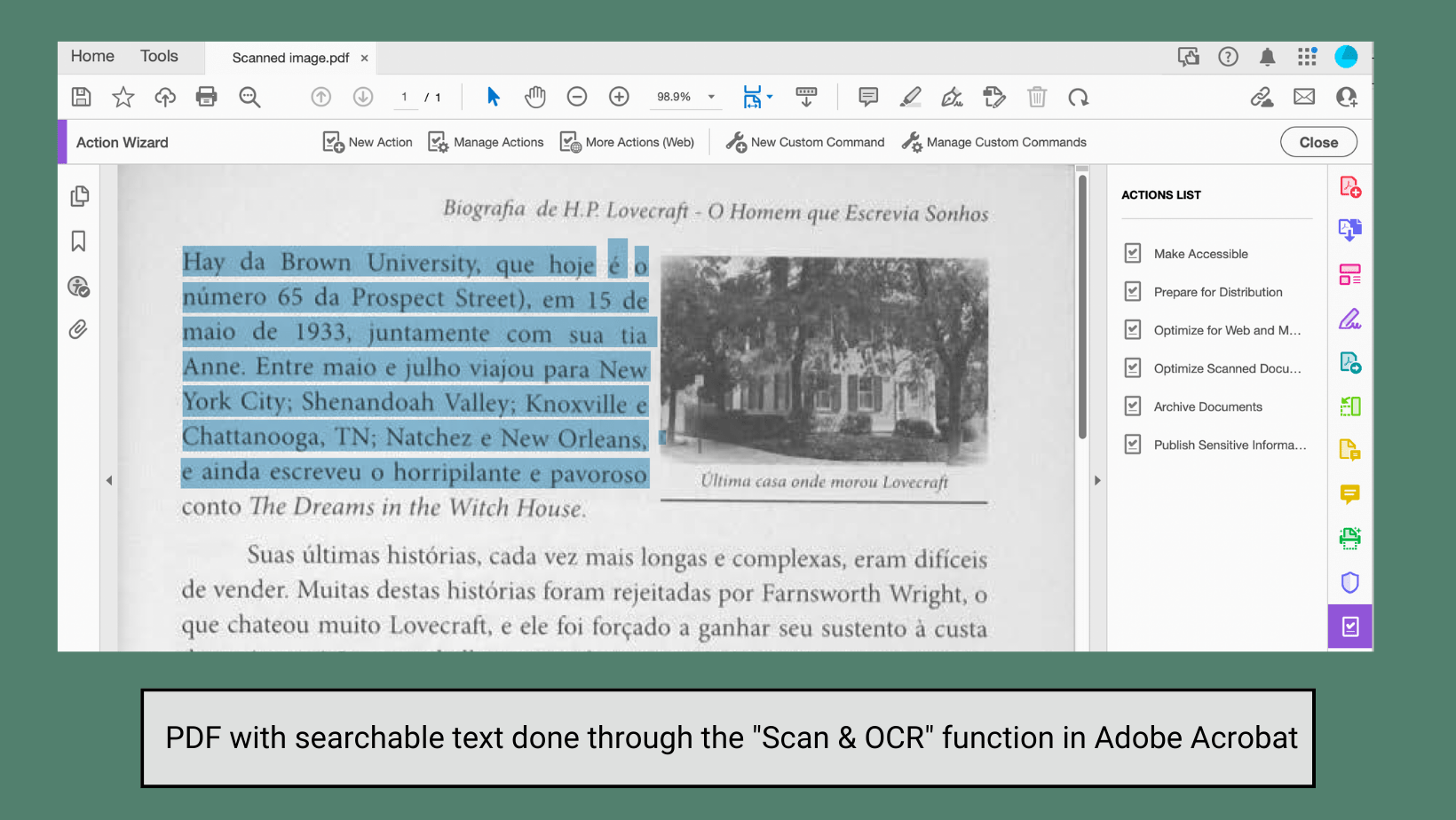
To create a Canvas sandbox course, you can follow the directions listed in this UWGB Knowledge Base article. There are, however, a few caveats for the creation of a sandbox course in the UWGB instance of Canvas. These conditions are listed below:

- You must be enrolled in at least one existing Canvas course as a Teacher. If you are not enrolled in any Canvas courses as a Teacher yet, you can email DLE@uwgb.edu to have a Canvas admin create a sandbox for you.
- You must access the Sandbox course creation tool, located under the Help menu within the Canvas Global Navigation Menu, from the University of Wisconsin – Green Bay instance website (https://uwgby.instructure.com).