Accessibility involves designing materials so that as many people as possible can engage with them, regardless of users’ physical or cognitive abilities. Meeting baseline accessibility standards is key to inclusive course design, and the digital age has made it faster and easier than ever to create accessible materials. Small changes to a document, like using a clear font and appropriately-sized text, can significantly improve the user experience. To get you started, we have assembled a list of some critical “dos and don’ts” of digital accessibility, along with guides from Microsoft Word, Microsoft PowerPoint, and Canvas for each category.
Contents
Text Styles
Do… ✅
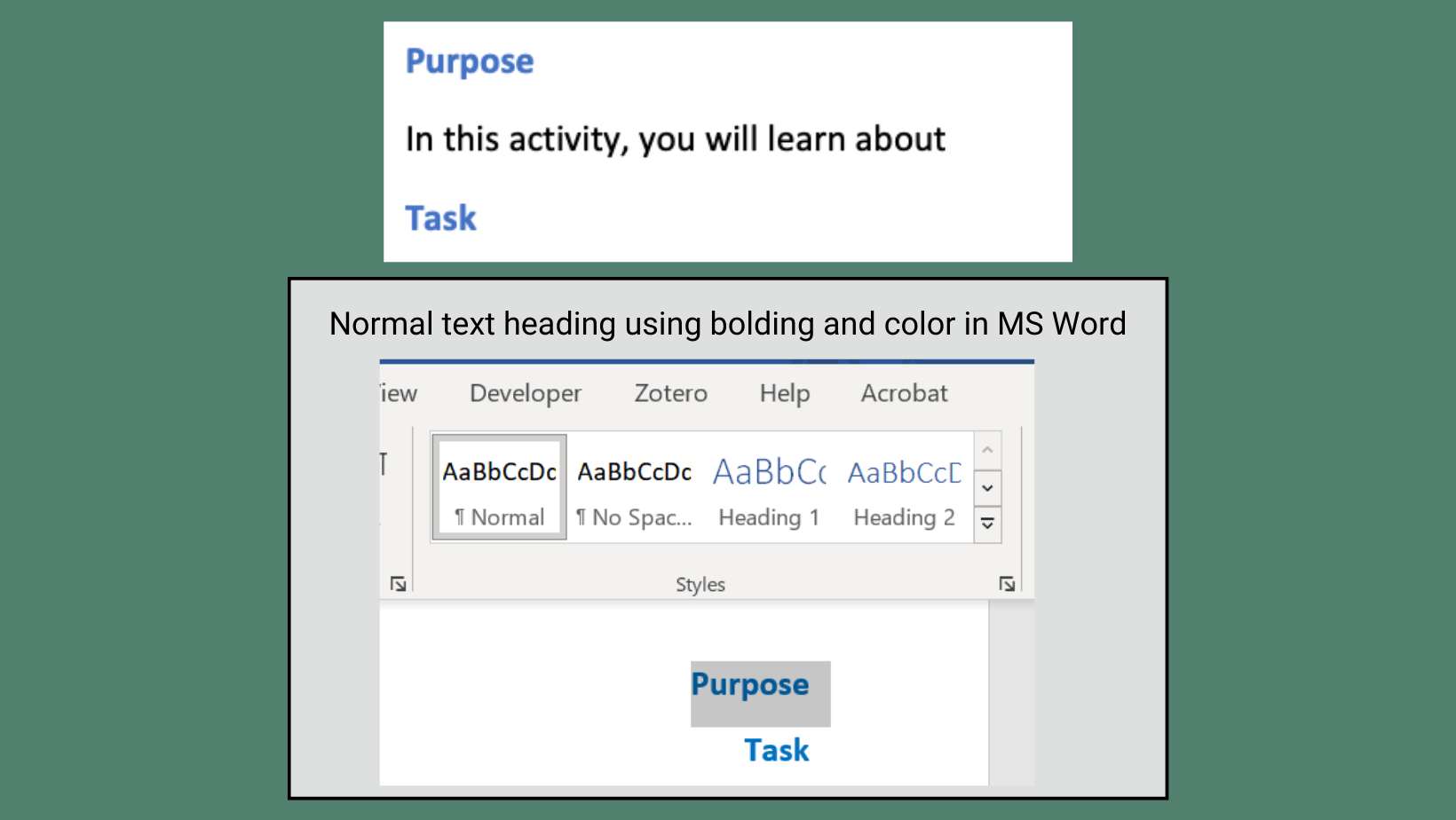
Use bold or italic styling sparingly to emphasize words or short phrases within the body of a text. To call attention to an entire sentence or section, consider writing “Important” before the content.
Use underlining only for hyperlinks to assist people who are color blind in differentiating them from regular text. Similarly, avoid using text color and highlighting alone for emphasis as they may be challenging to distinguish. Some screen readers do not announce bold or italicized text, so refrain from using text styles alone to create meaning.
Headings & Document Structure
Do… ✅
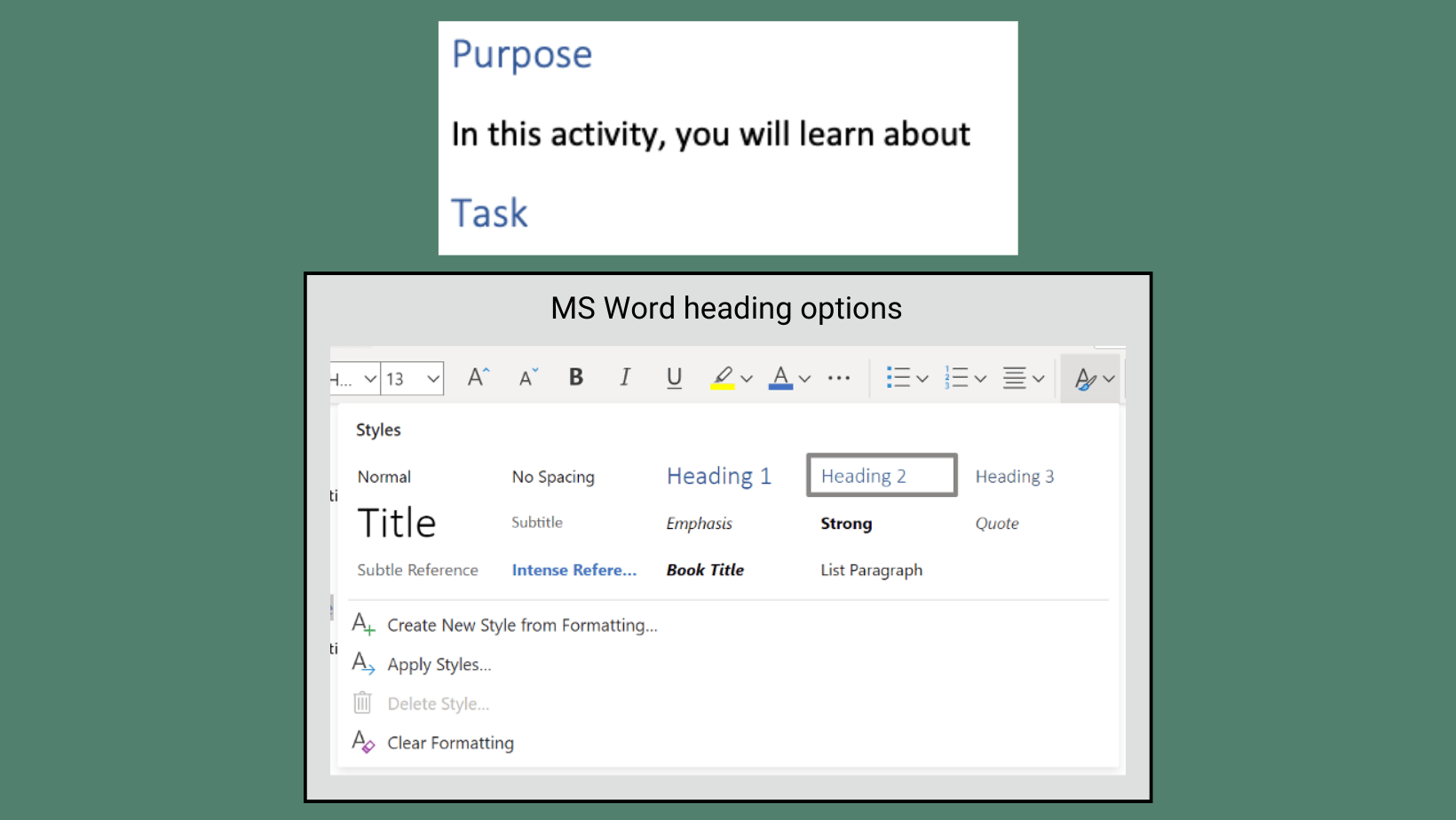
Use built-in heading styles in Word and the Canvas Rich Content Editor to organize content hierarchy. In PowerPoint, make sure to use an accessible template, add a title to every slide, and double-check slide reading order.
The built-in heading styles in these applications add special HTML code that makes it easier for people who use assistive tools to navigate a document.
Links
Do… ✅
Create concise hyperlinks with text that identifies or describes the link in a self-contained way.
Providing meaningful links helps people understand what to expect when they click the link. It also makes it easier for users who rely on assistive technology to navigate between links.
Images
Do… ✅
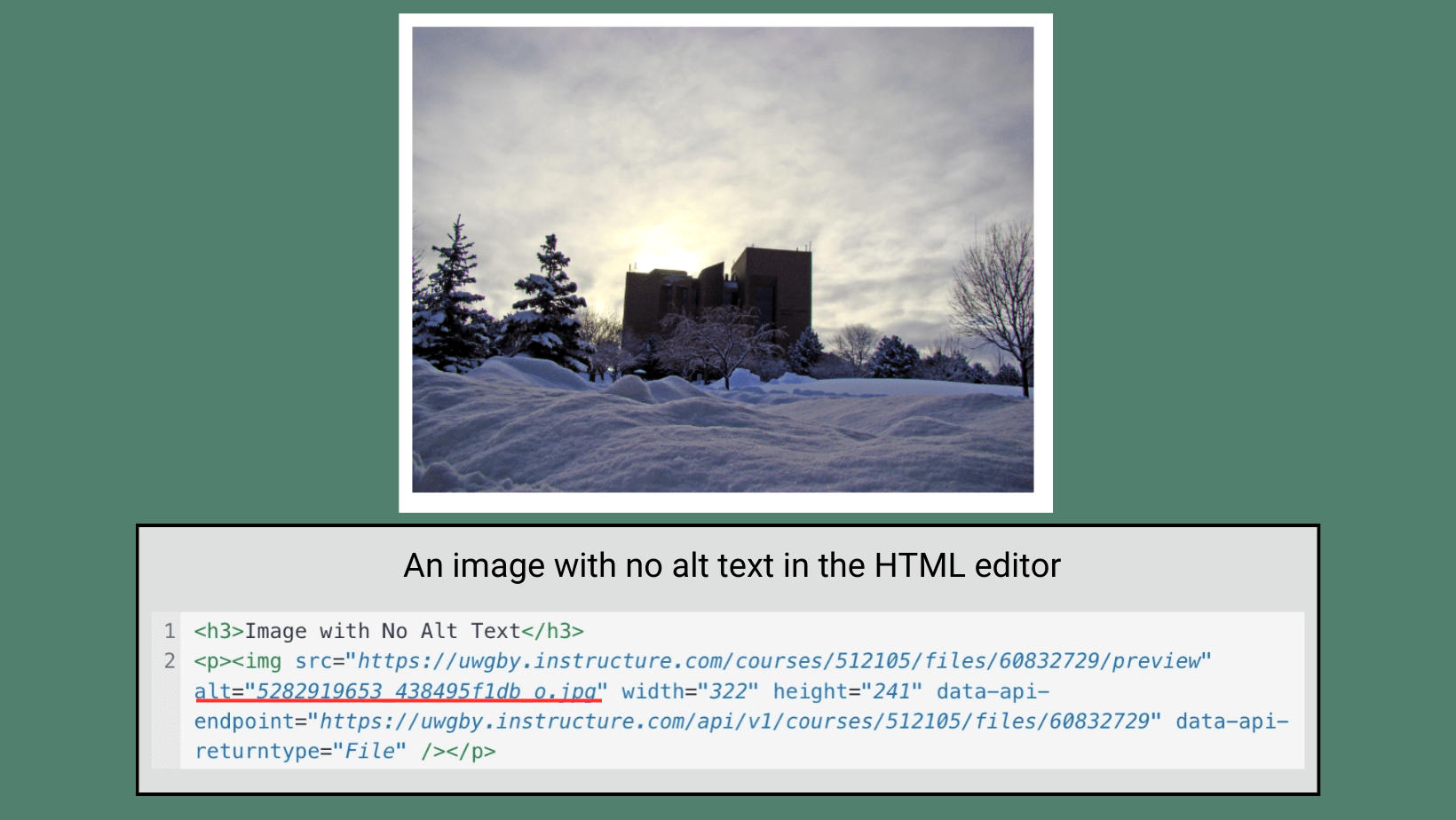
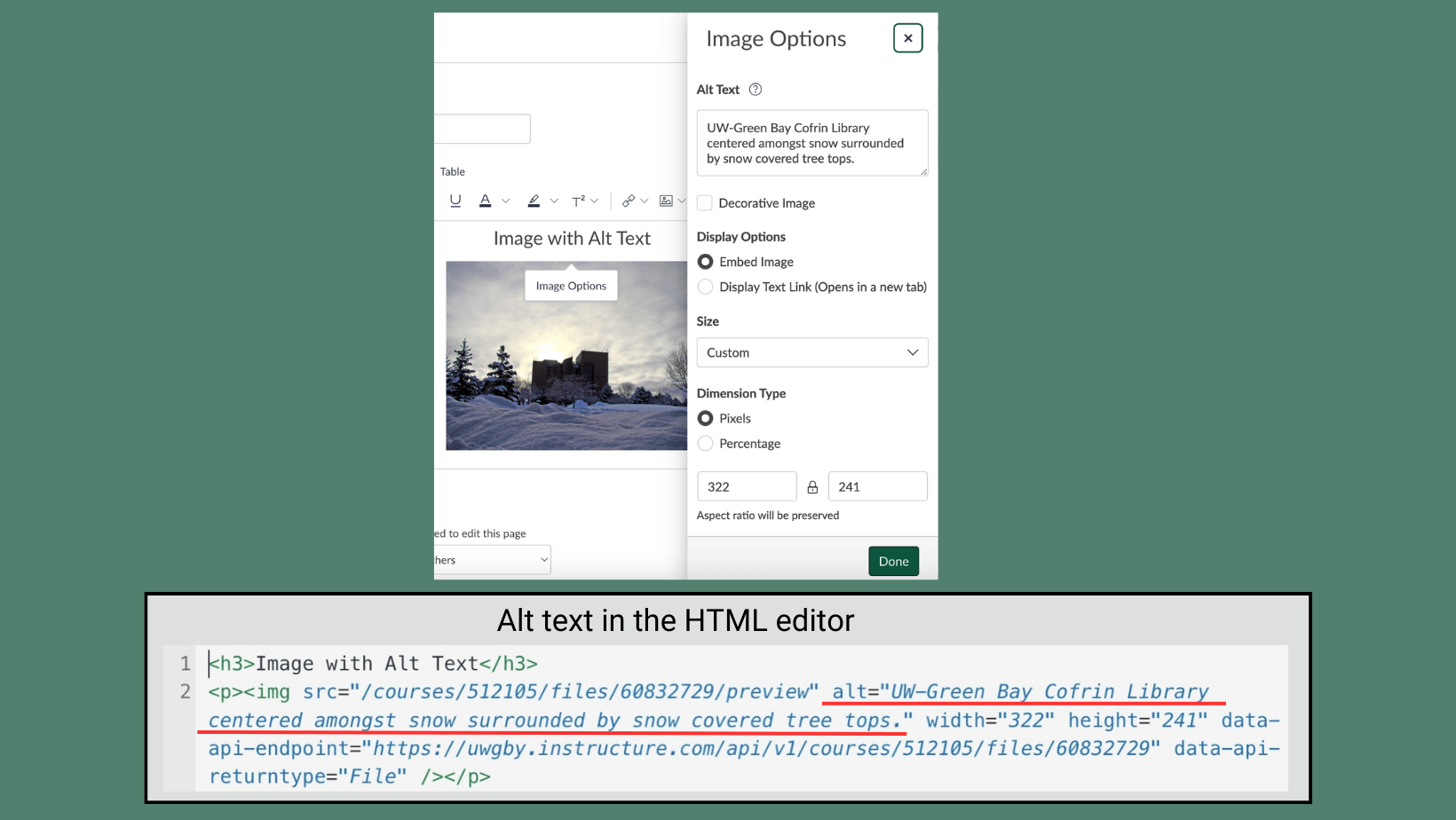
Add alt text or captions to describe images that convey information in Word, PowerPoint, and Canvas. Mark other images as “decorative” so they are ignored by screen readers.
Providing alt text or a caption helps people with low or no vision understand images.
Audio & Video
Do… ✅
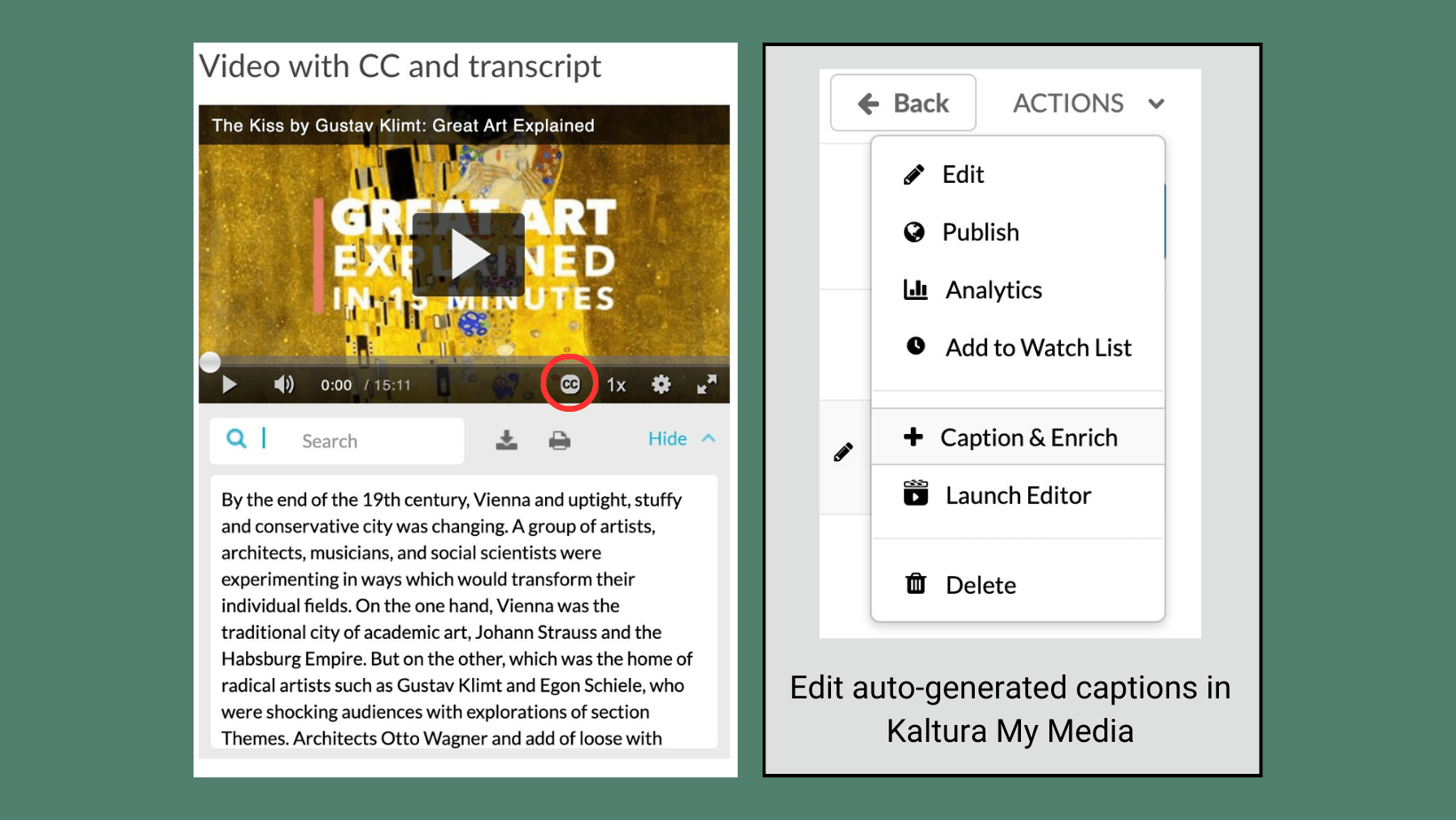
Upload your recordings into Kaltura (My Media) for automatic captions or search for media that is captioned. For spoken audio that does not have a visual component, such as a podcast stream, provide a transcript instead.
Captions and transcripts allow people with limited or no hearing to engage with audio and video media, plus they benefit those with other access barriers. Users can also benefit from having a searchable transcript.
Lists
Do… ✅
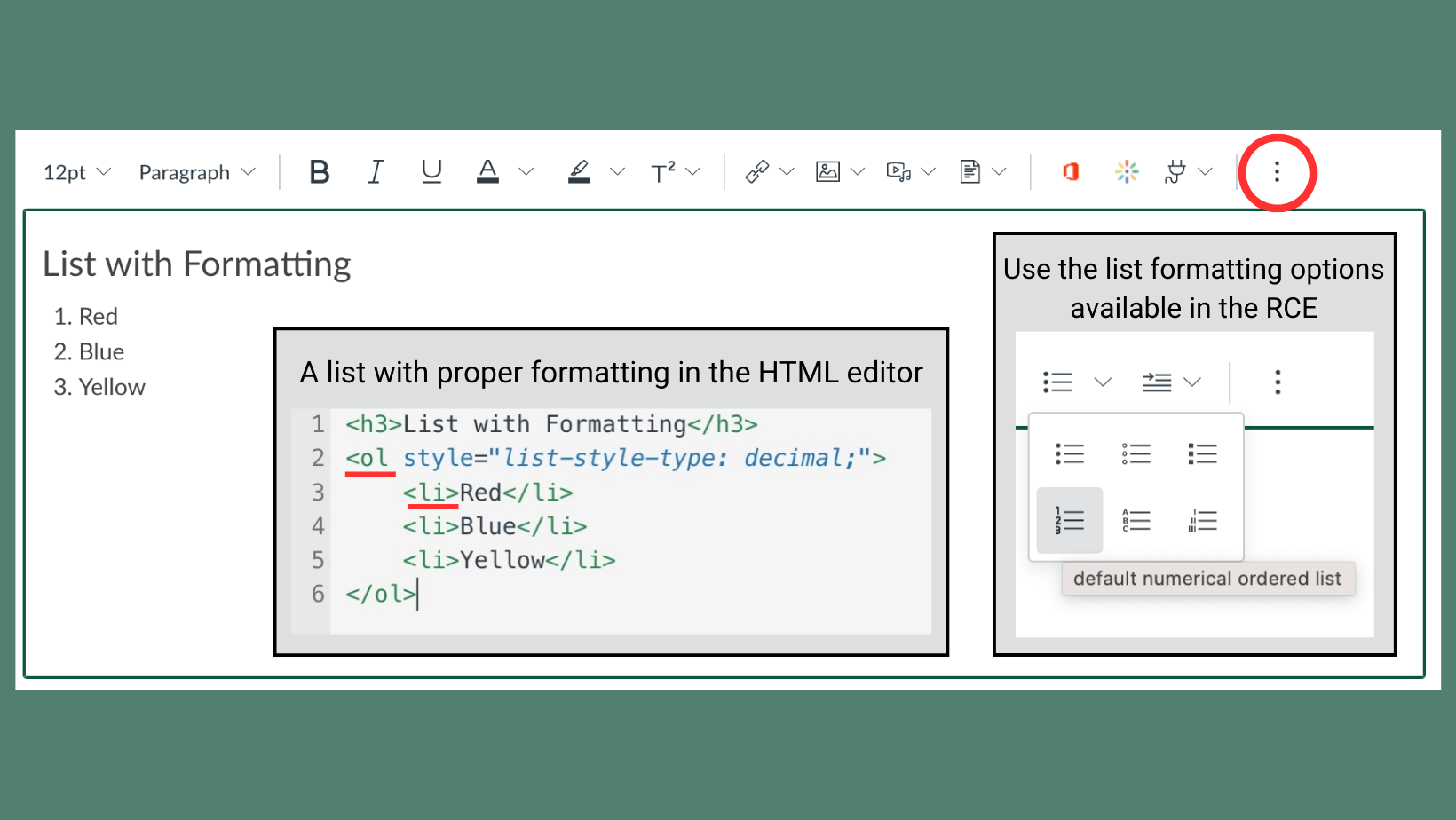
Use the bullet and numbering buttons in the toolbars of Word, PowerPoint, and the Canvas Rich Content Editor.
The built-in list formatting options in these applications add special HTML code that makes it easier for people who use assistive technologies to navigate a document.
Tables
Don’t… ❌
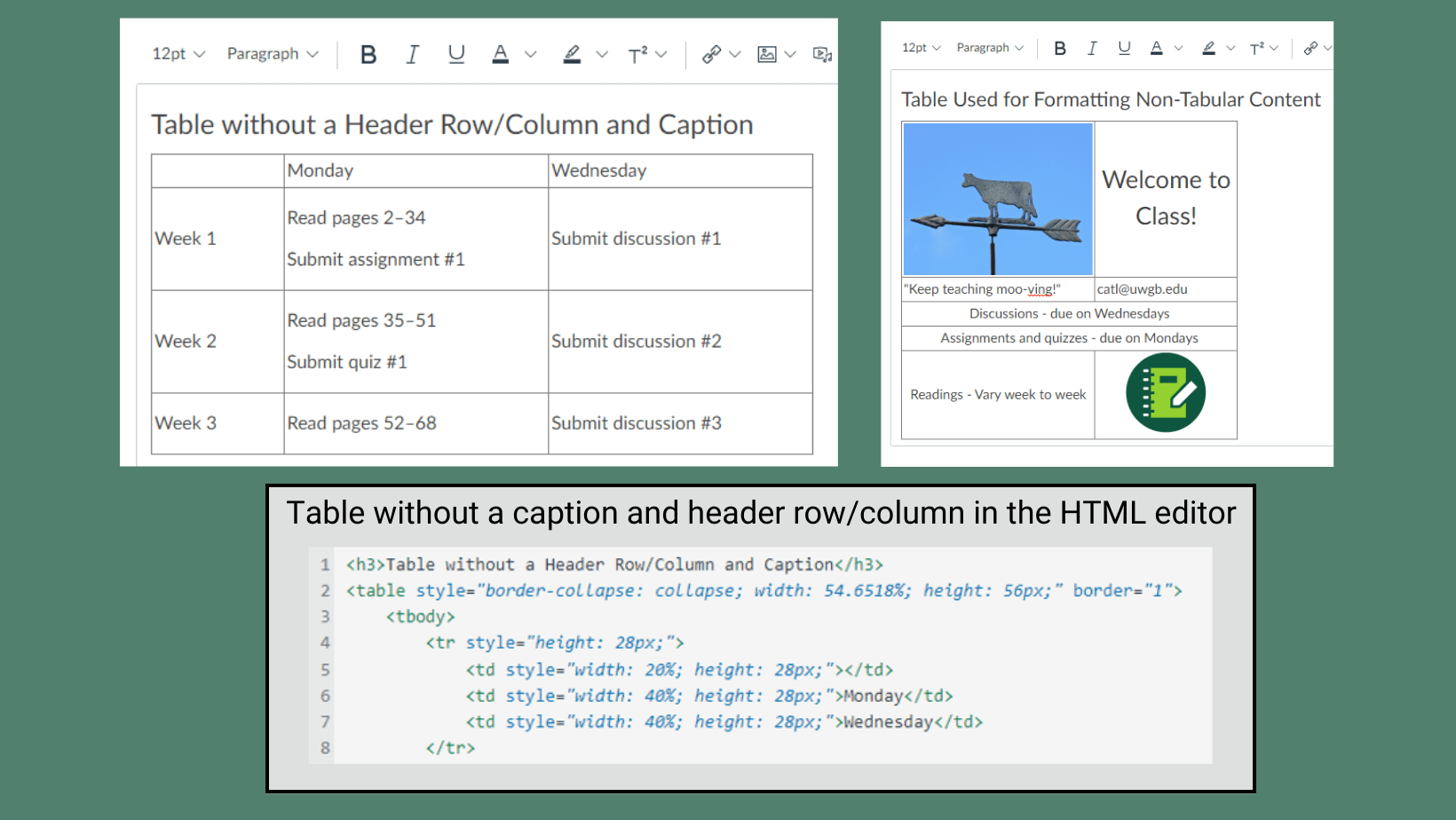
Subdivide and merge cells, omit captions and row/column headers, or use tables as a “hack” for formatting content.
Do… ✅
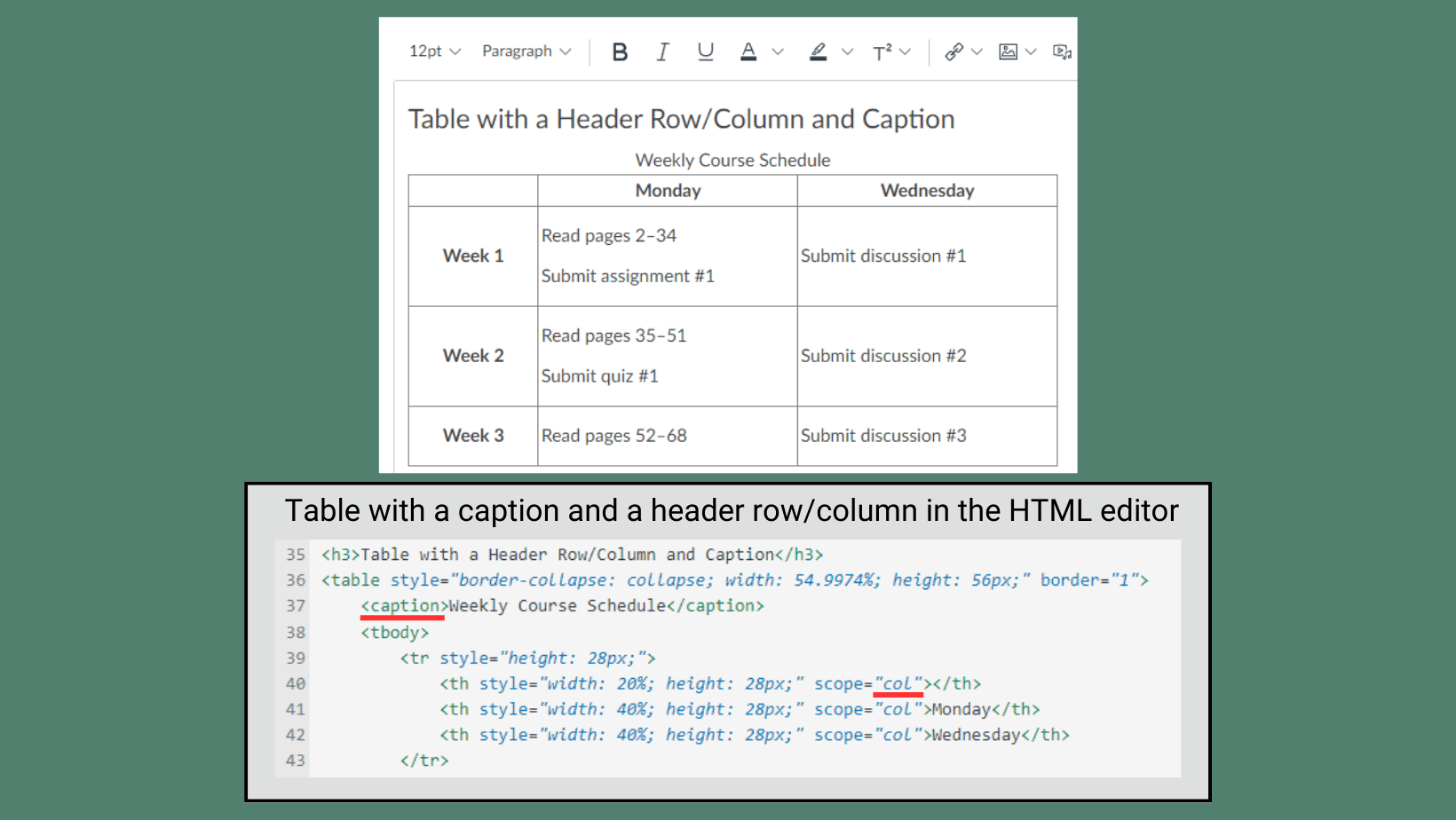
Use tables to present data in rows and columns with a logical layout. Use the built-in tools in Word and the accessibility checker in the Canvas Rich Content Editor to include a caption and set a header row and/or header column for data tables. Avoid using tables in PowerPoint if possible, but if you do, follow these guidelines.
Adding a caption and setting a header row/column with the built-in formatting options adds special HTML code that helps users who rely on assistive technology understand and navigate the table. Screen readers may struggle to interpret the layout and hierarchy of the information presented when tables are used to format content other than data. Subdivided and merged cells also pose challenges for users that navigate with a keyboard or rely on screen readers.
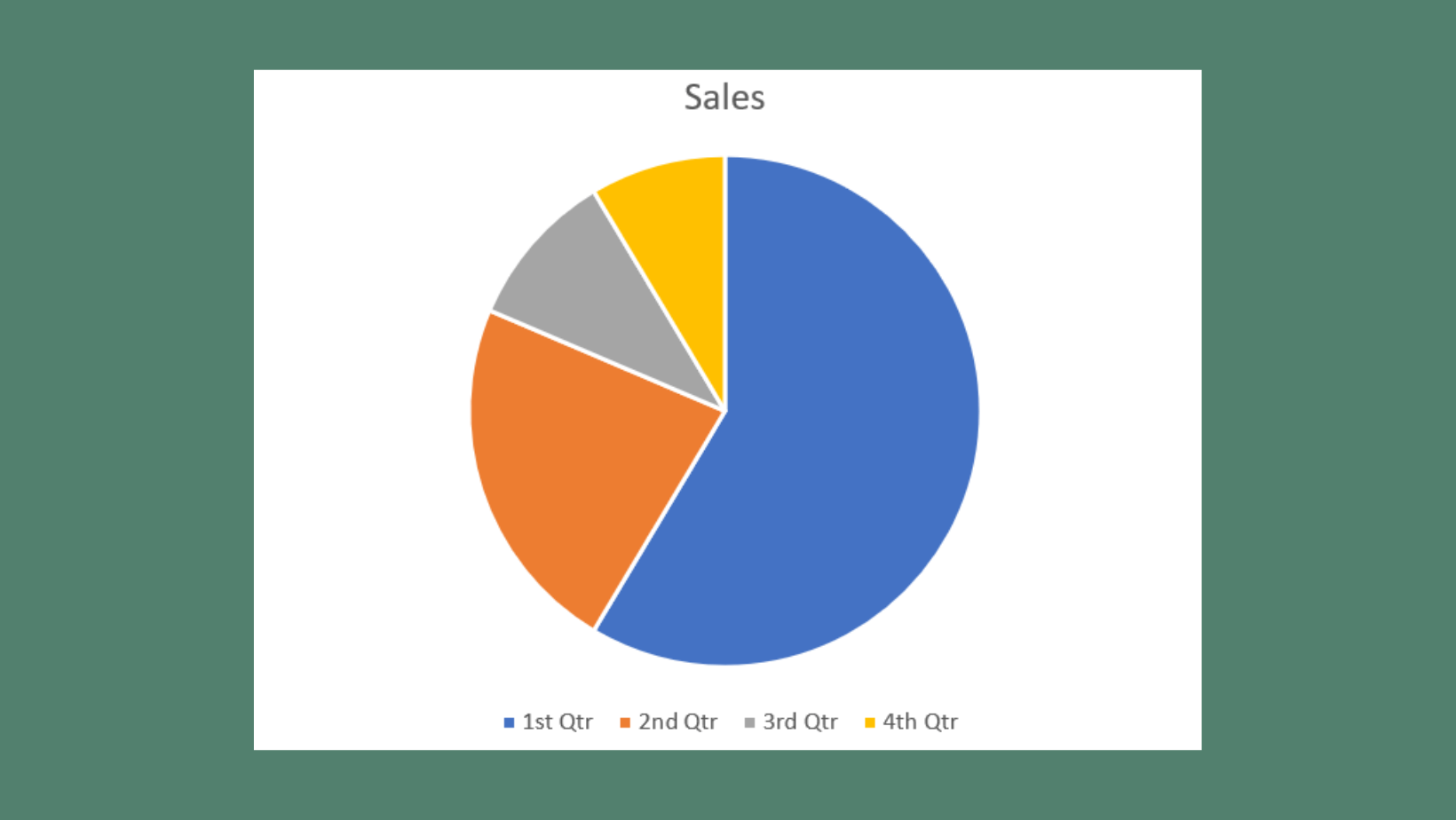
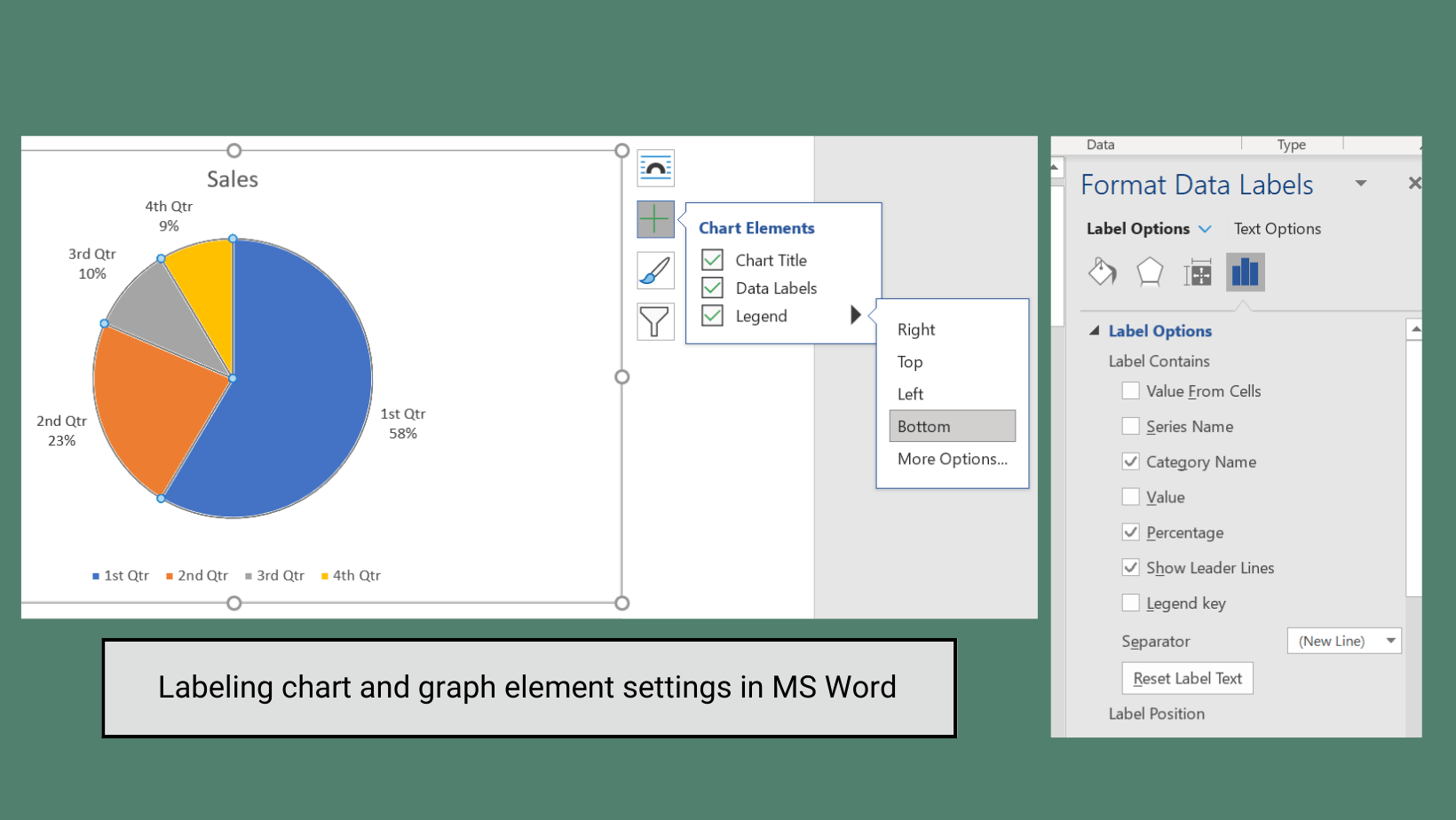
Charts & Graphs
Do… ✅
Directly label elements in charts and graphs and/or use shapes or patterns to differentiate elements.
People who are color blind or who have low vision may have trouble differentiating colors.
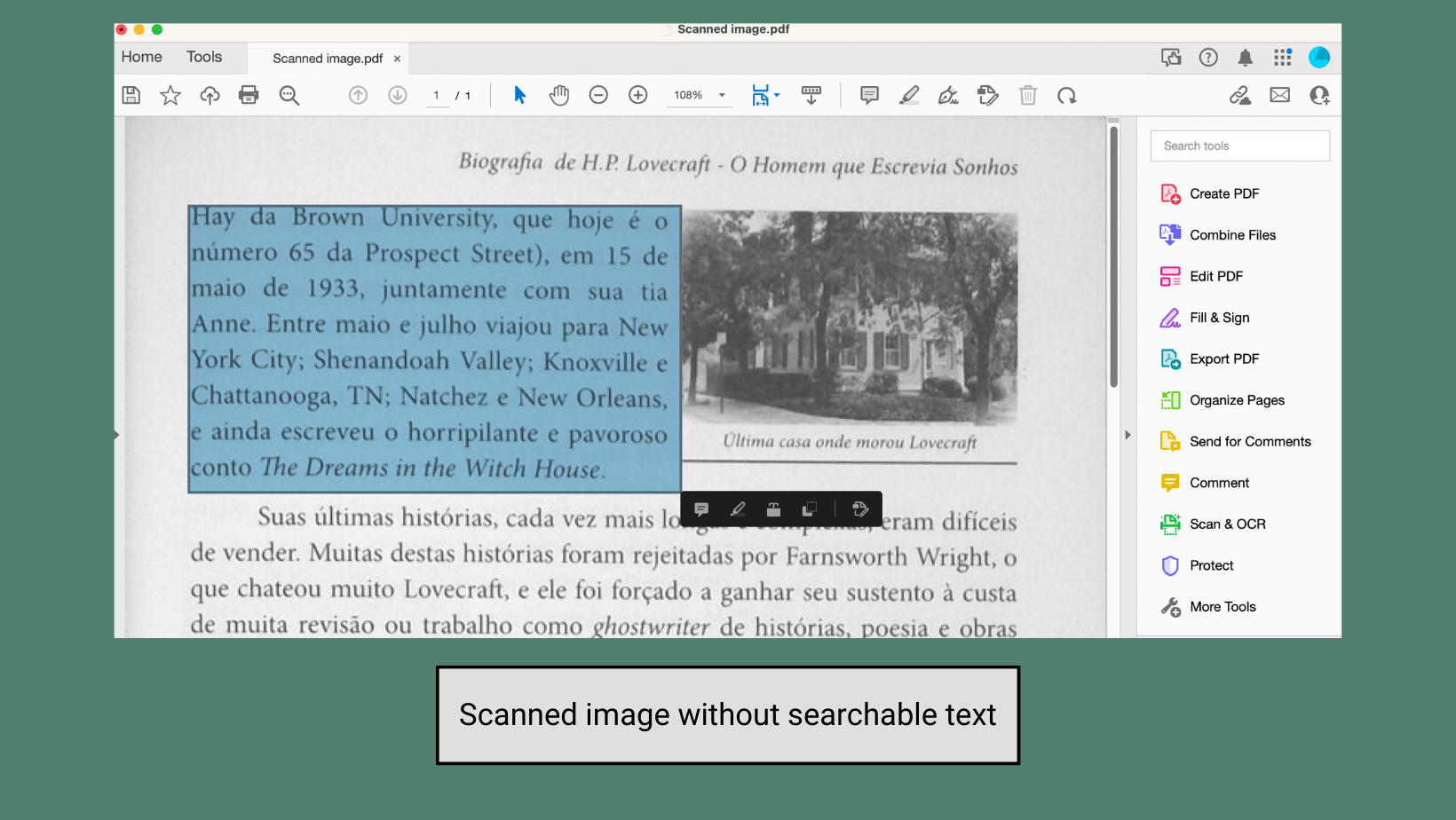
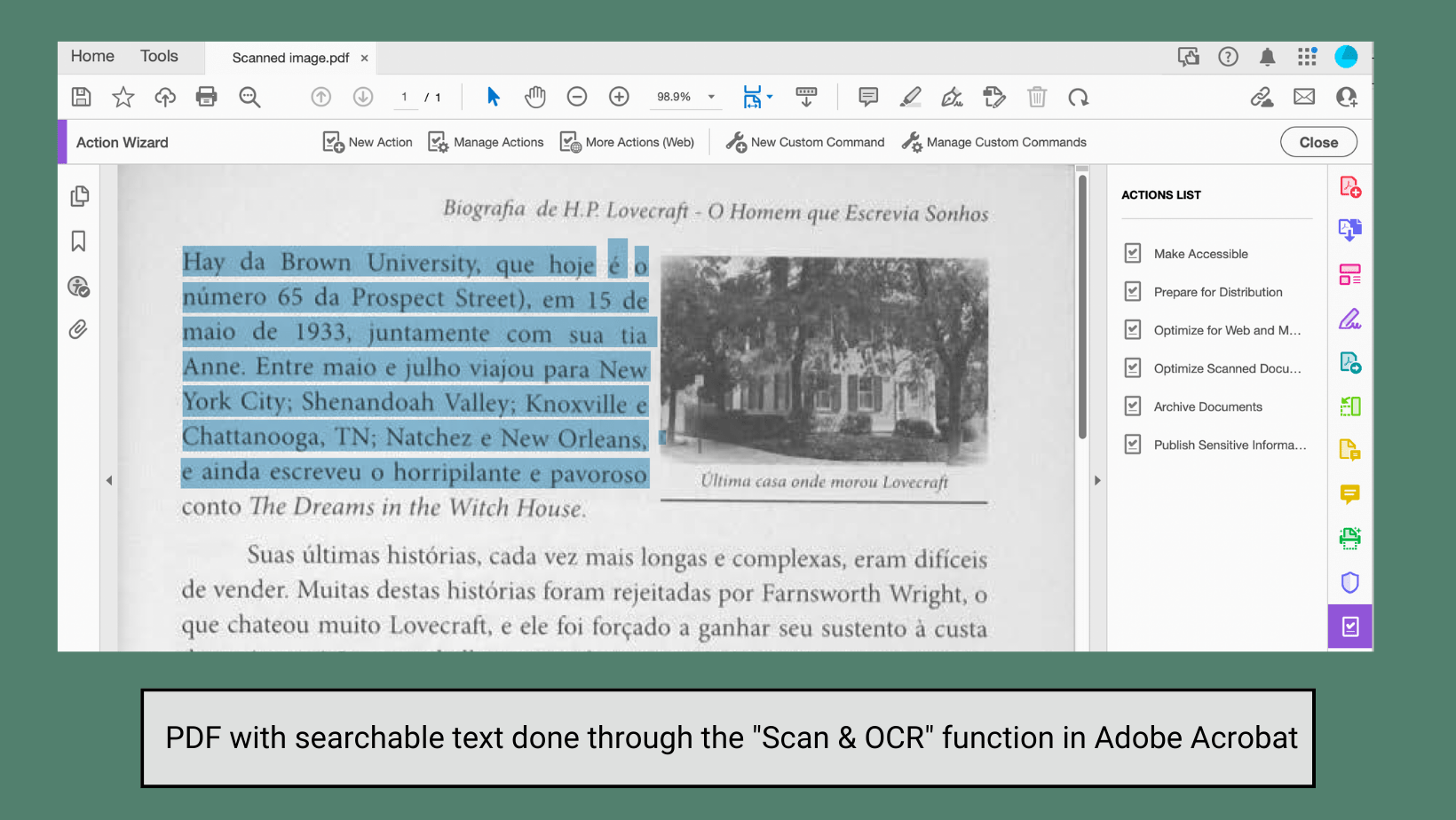
Scanned Documents
Do… ✅
Find an alternative accessible resource or use the optical character recognition (OCR) tools in Adobe Acrobat to turn a scan into an accessible PDF with selectable text and a logical reading order.
Digital scans of physical texts are encoded like images and are not readable by most screen readers. OCR converts a scanned document into a format that allows people who use assistive technologies to engage with the text, plus it benefits all users by making the document searchable.
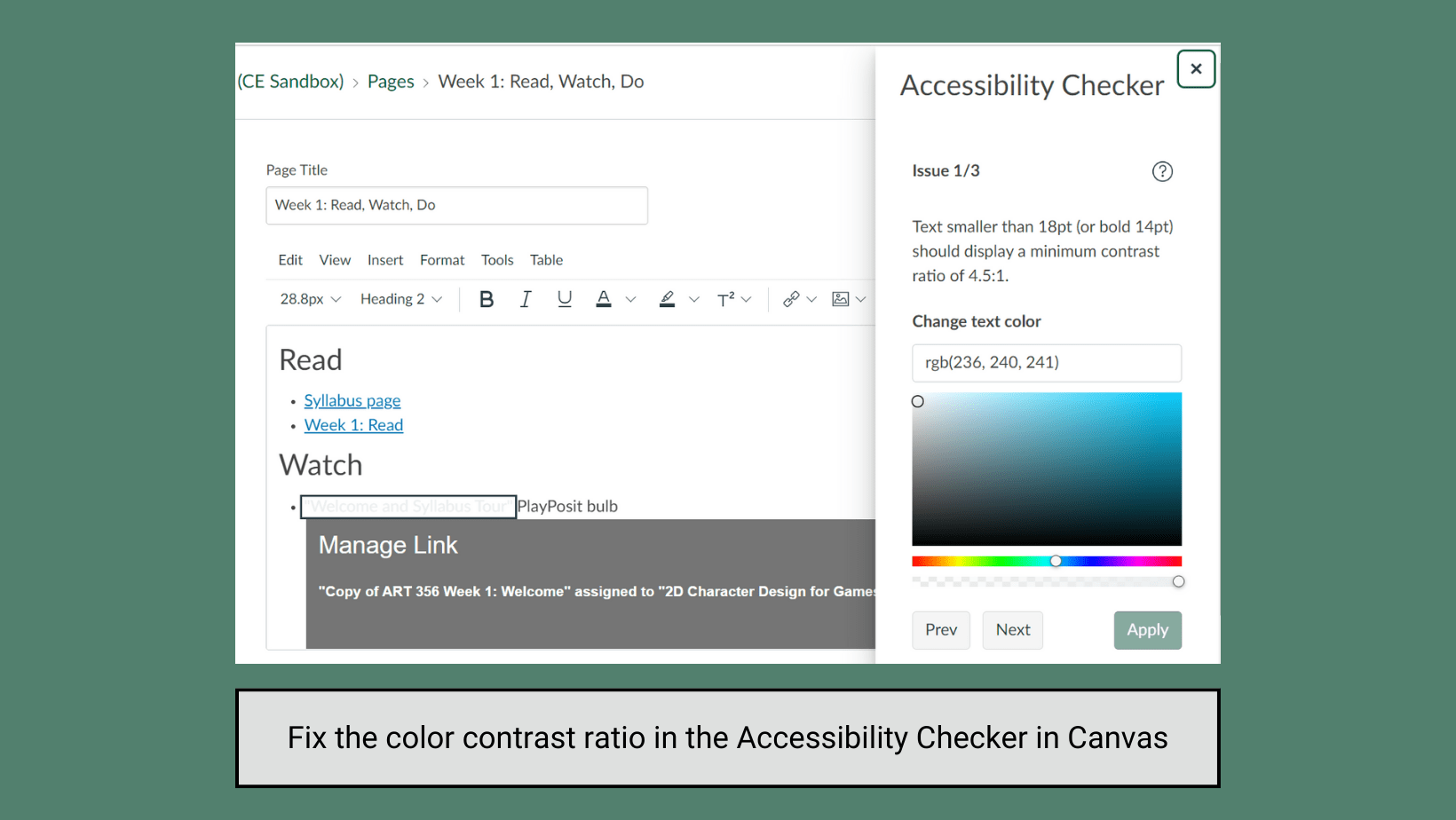
Accessibility Checkers
Do… ✅
Use the accessibility checker tools in Word, PowerPoint, and Canvas to scan for and repair common issues – including many of the issues described in this resource – before exporting, publishing, or sharing materials. For Canvas, you can also use the UDOIT accessibility checker to scan your whole course.
Using built-in accessibility checker tools can help ensure that your course materials meet accessibility standards.
Resources by Application
For accessibility resources specific to Word, PowerPoint, and Canvas, respectively, please see the guides and tip sheets below:
-
-
- Make your Word documents accessible to people with disabilities (Microsoft Support)
- Make your PowerPoint presentations accessible to people with disabilities (Microsoft Support)
- Canvas – General Accessibility Design Guidelines (Canvas blog post)
-
Need Help?
This resource is meant to be a starting point for best practices in digital accessibility, but if you have questions beyond the scope of this guide, we welcome you to reach out to CATL! Send us an email at CATL@uwgb.edu or fill out our consultation request form to discuss digital accessibility in your own courses.