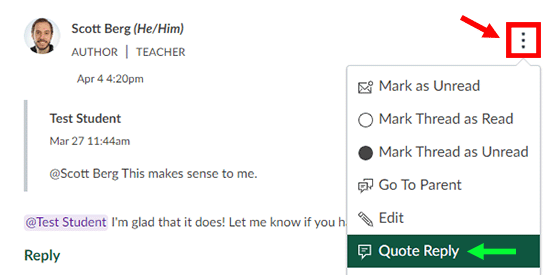
Welcome to our GAI resource-sharing blog page! Here you’ll find some of the latest updates and articles on generative AI, curated especially for faculty and instructional staff. While there are numerous resources available out there, CATL will share a select, timely sample of articles and perspectives to help instructors stay informed about new changes in AI technology and education.
For more in-depth, instructor-focused articles on generative AI by CATL, explore our AI Toolbox Articles.
Table of Contents
Generative AI Tools Directory
Stay updated on the different AI tools being created and discover what your peers or fields might be using!
Trends in AI
(Resources in this section are updated biannually)
May 2023 – June 2024
- Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Teaching and Learning, May 2023. This report by the Office of Educational Technology provides insights on how AI can be integrated into education practices, and recommended responses for educators.
- The AI Index Report: Measuring trends in AI, April 2024. Created by the Institute for Human-Centered AI at Stanford University, this report provides an analysis of AI trends and metrics, including important insights into the current state and future direction of AI for educators grappling with the rapidly evolving technology and what it means for their teaching practices.
- AI in 2024: Major Developments & Innovations, Jan. 3, 2024. This article provides a timeline of AI developments during 2023 and newest updates in 2024.
- 2024 AI Business Predictions, 2024. This report by PwC describes how businesses are preparing for and incorporating AI, with predictions on future trends and AI strategies in the corporate world.
Monthly Resources for Educators
(Resources in this section are updated for each month)
June 2024
Tips for Teachers
- If you haven’t signed into Copilot with your UWGB account, now is the time! Microsoft Copilot, accessible through any browser and soon integrated into Windows 11, avoids using your personal email, which makes it a better alternative for classes. It doesn’t require providing, for example, a personal cellphone number for use, and it is available to all UWGB faculty, staff, and students with an institutional login and ID. Copilot also offers enhanced data protection when logged in using your UWGB account, although FERPA-protected and personally identifiable information should still not be entered. Watch this short video on how to log in. Remember, use any AI tool responsibly and always vet outputs for accuracy.
Latest Educational Updates
- Latest AI Announcements Mean Another Big Adjustment for Educators, June 6, 2024. This article from EdSurge recaps some of the latest AI advancements that will heavily impact education and provides advice from instructors and ed tech experts on how to adapt.
- AI Detectors Don’t Work. Here’s What to Do Instead, 2024. MIT’s Teaching & Learning Technologies Center critiques AI detection software and suggests better alternatives. The article advocates for clear guidelines, open dialogue, creative assignment design, and equitable assessment practices to effectively engage students and maintain academic standards.
May 2024
Tip for Teachers
- Subscribe to the “One Useful Thing” blog by Ethan Mollick, an Associate Professor at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania and Co-Director of the Generative AI Lab at Wharton.
Latest Educational Updates
- Introducing ChatGPT Edu, May 30, 2024. OpenAI has announced their latest version of ChatGPT tailored specifically for universities (faculty, staff, and students).
- HESA’s AI Observatory: What’s New in Higher Education, May 19, 2024. View some of the latest developments regarding AI’s role in higher education and how instructors are responding to new trends and taking new approaches in the classroom.
- How generative AI expands curiosity and understanding with LearnLM, May 14, 2024. Google has introduced LearnLM, a new family of Gemini-based models rooted in educational research and designed for both instructors and students.
- Towards Responsible Development of Generative AI: An Evaluation-Driven Approach, May 5, 2024. This paper by Google explores how GAI tools like Google’s LearnLM-Tutor could be used in higher education as personal tutors and teaching assistants. The researchers also propose a comprehensive framework for evaluating GAI tools in these contexts.
Latest AI Tech Advancements
- Google I/O Wrap-Up: Gemini AI updates, new search features, and more (CNBC), May 14, 2024. Google announces new updates to Gemini AI, new search features, and more.
- OpenAI Launches ChatGPT 4o, May 13, 2024. Read more about OpenAI’s newest ChatGPT update, “4o,” which brings some of the advanced features of GPT-4 to free users. Future updates are set to include increased audio/video features and multimedia outputs.

 When Professor Lybbert began thinking about escape rooms, they were all the rage. She discovered an article in the Journal of Chemistry Education, which described, in detail, a Lab-Based Chemical Escape Room. The article describes a scenario in which four bombs are set to explode unless the chemists in the room are able to neutralize them. The scenario presented used the kinds of puzzles those familiar with escape rooms might be used to, but in order to solve these puzzles, chemistry knowledge would also come into play. This is what Professor Lybbert used as a guide to create her own physical escape room inside her classroom. More than just creating a fun activity, she created an environment designed to immerse her students in the escape room, complete with yellow caution tape, scary music, and a countdown timer. Her students get a full hour to work as a team to solve this puzzle.
When Professor Lybbert began thinking about escape rooms, they were all the rage. She discovered an article in the Journal of Chemistry Education, which described, in detail, a Lab-Based Chemical Escape Room. The article describes a scenario in which four bombs are set to explode unless the chemists in the room are able to neutralize them. The scenario presented used the kinds of puzzles those familiar with escape rooms might be used to, but in order to solve these puzzles, chemistry knowledge would also come into play. This is what Professor Lybbert used as a guide to create her own physical escape room inside her classroom. More than just creating a fun activity, she created an environment designed to immerse her students in the escape room, complete with yellow caution tape, scary music, and a countdown timer. Her students get a full hour to work as a team to solve this puzzle.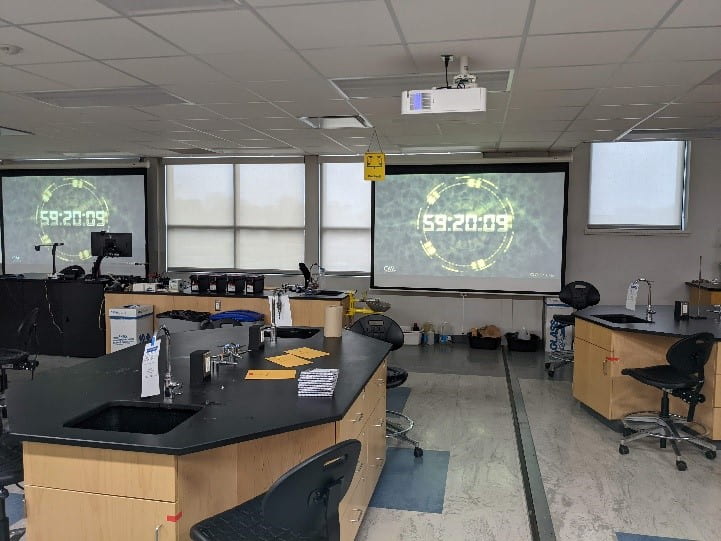
 Students have the opportunity to use the knowledge they’ve gained throughout the course of the semester in a low-stakes (but heightened-intensity) lab activity that gives them the chance to reflect on their learning once the adrenaline has passed. Although not perfectly a real-world scenario, students do realize that they can use their knowledge when the time counts!
Students have the opportunity to use the knowledge they’ve gained throughout the course of the semester in a low-stakes (but heightened-intensity) lab activity that gives them the chance to reflect on their learning once the adrenaline has passed. Although not perfectly a real-world scenario, students do realize that they can use their knowledge when the time counts!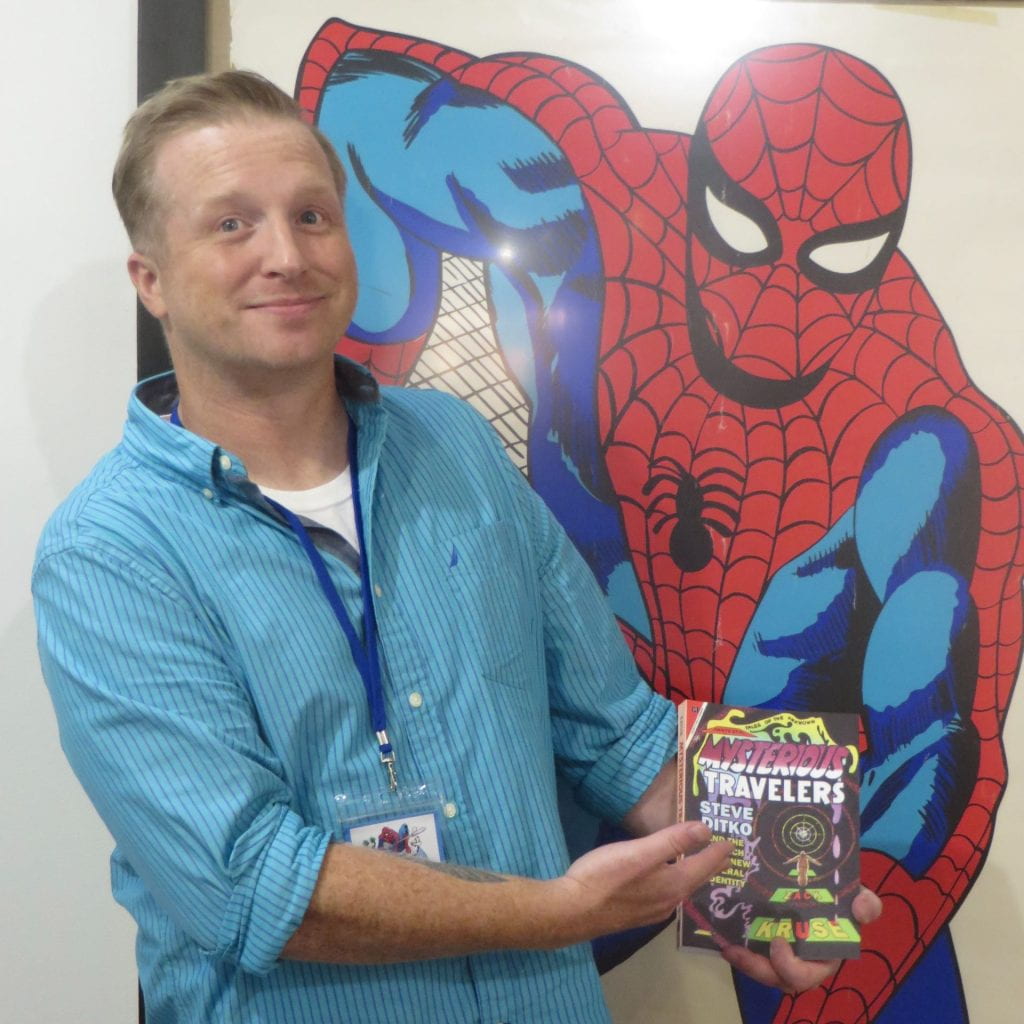


 Professor Kruse has used the following comic books in his classroom. Some of those comic studies have included author visits. Professor Kruse uses a multitude of others not listed here and would be happy to offer recommendations if you’d like to integrate some of these works into your own classroom.
Professor Kruse has used the following comic books in his classroom. Some of those comic studies have included author visits. Professor Kruse uses a multitude of others not listed here and would be happy to offer recommendations if you’d like to integrate some of these works into your own classroom.