PlayPosit has many potential applications for teaching, so it can be overwhelming to decide how you might use it in your own course. We’ve collected some use cases spanning a range of disciplines and course formats as a way to help you think about how other instructors are already using the tool, and then, by extension, how you might adopt it for your own teaching style and content area. The use cases below are organized by four of PlayPosit’s features:
- Core Platform, which refers to PlayPosit’s interactive video builder and player used for asynchronous learner engagement
- Broadcast, which is PlayPosit’s live audience response system used for synchronous learner engagement
- Learner Made Content, which refers to PlayPosit bulbs or interactions created by learners and assessed by instructors
- Peer Review, in which learners review and provide feedback on PlayPosit content created by their peers
Core Platform (Asynchronous Learner Engagement)
Knowledge Checks
One of the most common ways to use PlayPosit’s main platform is to add knowledge checks to videos. These knowledge checks might be as simple as an objective true-false question, or as complex as a subjective free response question requiring students to reflect, analyze, or extrapolate.
Since PlayPosit bulbs can be either graded or ungraded, you can pick the option that works best for the function of the bulb. If you wish to keep the knowledge checks in your lectures low-stakes and for the sole benefit of the users, they might remain ungraded. Alternatively, perhaps you wish to replace some of your formative assessments (e.g. a post-lecture quiz) with an in-lecture quiz in the form of a PlayPosit bulb, in which case you would want to create a graded item. Learn more about graded and ungraded bulbs, as well as the types of interactions available, in this other PlayPosit toolbox article.
Engagement Checks
Another way to keep your PlayPosit interactions low stakes is to use engagement checks, rather than knowledge checks. In distance learning environments, instructors often worry that students won’t watch their videos. PlayPosit interactions can be built in to ensure just that. For these scenarios, you might make use of the poll and pause point interaction types in particular.
Polls function like a multiple-choice question but with no correct or incorrect answers. Since there are no right answers, polls are a simple, low-stakes way to add student engagement your bulbs. If the bulb is graded and you add a point value to the polling interaction, students are awarded points simply for responding.
Pause points are interactions where students simply have to click a button to continue. Pause points might be useful for adding extra tips or reminders or linking to external resources. Like polls, if you add a point value to the interaction, students will receive full points for simply “completing” the interaction when used in a graded bulb.
Learner Notes
The notes feature is not an interaction type, but a default feature built into the PlayPosit video player. Learners can add timestamped notes while watching PlayPosit bulb, making it easy for them to go back and review certain points of a bulb at a later time. It also lets learners add content like images, links, and equations to their notes. If you would like students to make use of this feature, consider adding a few pause point interactions to your videos with suggestions for what points to include in their notes, like an important equation or acronym. You can also use PlayPosit’s pre-built learner notes template from the template gallery.

Potential Use Cases
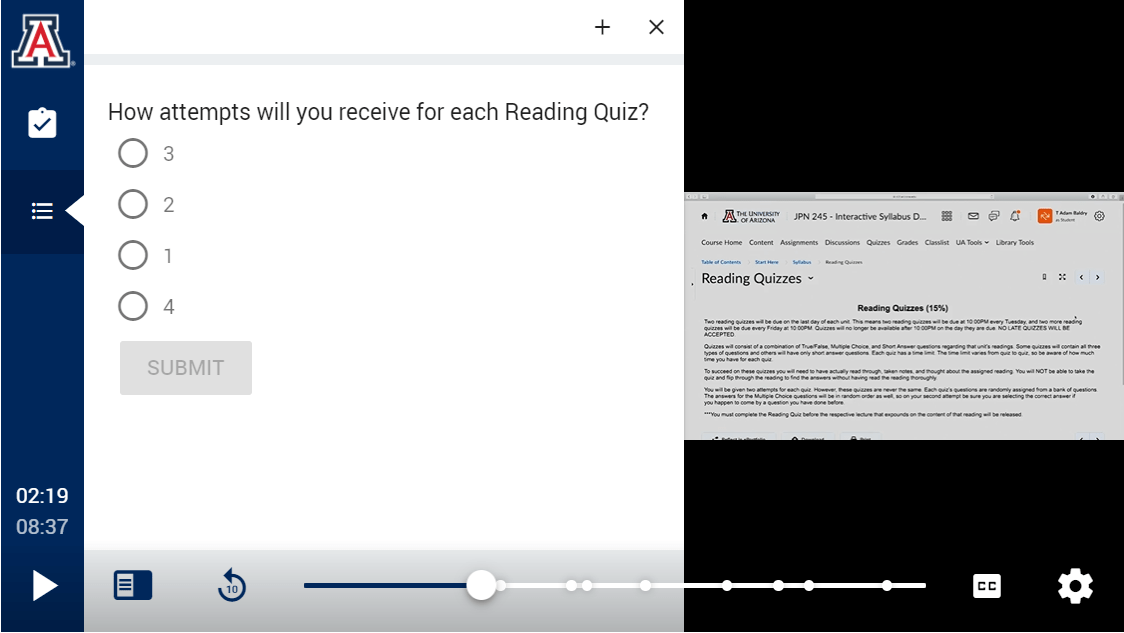
In the first session of a synchronous course, instructors often spend a good chunk of time going over the syllabus. With PlayPosit, you could instead record a syllabus overview video and then add knowledge checks with questions like, “when are office hours?” or “how many times can you take a quiz?”. See this example from the University of Arizona if you want to try it out from the learner’s perspective.
In both empirical studies and student surveys, the prevailing messaging around lecture videos is that shorter is better. If you have a 45-minute lecture recording, consider breaking it down into smaller chunks of 5–15 minutes and then delivering them as PlayPosit bulbs. Adding PlayPosit interactions can incentivize students to watch all the way through and help you track which students are interacting with the lectures.
Some instructors are moving away entirely from synchronous lectures, opting for pre-recorded content delivery. Synchronous class time, whether face-to-face or virtual, can then be used to answer student questions, go over homework, or hold class discussions instead. One way to start is by using bulbs for pre-lab training, in which you assign PlayPosit bulbs in advance that deliver the necessary background information needed to engage in a lab, studio, or other hands-on activity that takes place during class.
Several PlayPosit interactions or features allow asynchronous viewers to contribute their thoughts and questions. Instructors can review learner feedback to get a sense of what is working in the class and identify concepts that require additional review. See our follow-up posts from What Will You Carry Forward?, Collecting and Working with Mid-Semester Feedback, and Building Information Literacy and Racial Literacy Together for a few examples. The bulbs in each of these posts use a different type of interaction (pause point, discussion, and free response, respectively) so it may be worth taking a look at all three to compare.
Broadcast (Synchronous Learner Engagement)
The use cases in the previous sections make use of what PlayPosit refers to as its “core platform”, however, our license includes additional features. One of these features is “Broadcast“, PlayPosit’s audience response system. Unlike the core platform, Broadcast is used in synchronous learning environments.
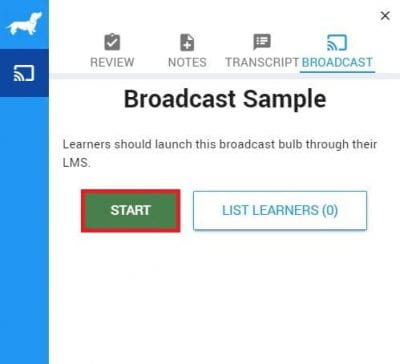
Broadcast allows instructors to push interactive learning content (quiz questions, polls, etc.) to both in-person and remote synchronous learners’ personal devices for real-time engagement and feedback. You can learn more about using Broadcast in this PlayPosit guide.
Potential Use Cases
Learner-Made Content
All of the examples up until this point have focused on instructor-made content, but did you know that you can have students create bulbs too? PlayPosit refers to bulbs, interactions, and other content made by students as “learner made content“, and student-created bulbs as “learner made bulbs ” (LMBs).
You can either have students select their own video for creating a bulb or provide them with a video link to use. In the latter scenario, students will add their own annotations or interactions to demonstrate their understanding of the video’s content. Another nice feature of learner-made bulbs is that the instructor can leave timestamped feedback on students’ bulbs. This could be particularly useful for student presentations, instrumental or vocal performances, or other activities that you would like students to record for assessment. You can learn more about creating assignments for learner-made bulbs in this PlayPosit guide.

Potential Use Cases
Some fields like nursing or counseling require a lot of instructor observation, which can prove challenging in distance learning environments. One nursing instructor was able to simulate one-on-one, face-to-face observation by having her students record their activities and then create PlayPosit bulbs out of the videos. The instructor could then provide timestamped feedback and supply additional resources if needed (images, links, etc.). Another instructor in counseling has her students use learner-made content in a very similar way.
Peer Review
Peer review builds on the previous feature, learner-made content. Like a regular peer review Canvas assignment, students first submit their own video to the PlayPosit peer review assignment and are then assigned peers’ video submissions to review and leave feedback.
One useful aspect of this tool is that student reviewers leave their feedback as discussion comments that are each timestamped to indicate the exact moment of the video when the reviewer paused and entered the comment. Instructors may additionally create a rubric for student reviewers to complete. You may also appreciate that PlayPosit requires reviewers to watch the video in full before submitting their review. As the instructor, you can view both the learner videos and the feedback left by other students and assign grades accordingly. Learn more about peer review in this PlayPosit guide.

Potential Use Cases
Questions?
As you explore PlayPosit, we encourage you to consult PlayPosit’s extensive knowledgebase of instructor guides, including this guide for Canvas users. You can contact PlayPosit support directly by clicking the “Contact” link on their support site and filling out their web form. PlayPosit also offers live trainings, webinars, and office hours. If you are interested in any of these vendor-led training opportunities, contact dle@uwgb.edu to learn more.
As always, we also welcome you to request a CATL consultation if you’d like to see a demo of PlayPosit or talk through how you might use it in your course.

