Engineering Details
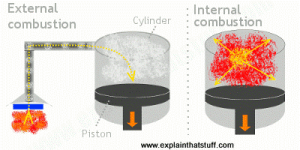
Heat engines are devices that convert heat energy into mechanical energy. Heat engines can be divided into two main classes. The first is ‘internal’ combustion engines where the heat is generated by the combustion of fuel inside of the engine. On the other hand, ‘external’ combustion engines are where the energy is passed into the engine from an outside source. An example of this would be the combustion of octane in our car engines. The fuel is burnt and exploded to create heat and energy which is sent to crankshafts in the engine that turn the axles, which in turn rotate the wheels to move the car. The efficiency of internal combustion heat engines is far better than external combustion engines because no energy is wasted is the process of transporting the heat from the outside source.
Leave a Reply