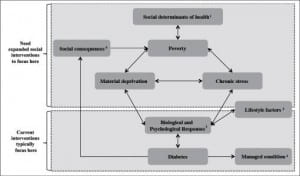
Cardiovascular disease- a condition that involve narrowed or blocked blood vessels that can lead to a heart attack, chest pain, or stroke.
There are several things you can do to prevent cardiovascular disease including eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, getting enough physical activity, not smoking or using tobacco products, and limiting alcohol consumption.
A healthy diet consists of eating plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables and eating less processed foods. Avoiding foods high in saturated fats, trans fat and cholesterol and high in fiber can help prevent high cholesterol. Another thing to do is to limit sodium intake which will lower blood pressure. Limiting sugar intake too can also lower blood sugar level to help prevent and help control diabetes. The best diet to follow is one full of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, nuts, fish, poultry and vegetable oils, drinking in moderation, not eating too much red and processed meats and refined carbohydrates. People who followed this diet had a 31% lower risk of heart disease. And a 20% lower risk of a stroke.
Keeping a healthy diet is important to maintaining a healthy weight. Being overweight increases ones chances of developing a heart disease. Waist size is also important because for people who are not overweight waist size will be an even better warning sign for increased health risks.
Another way of keeping a healthy weight is through physical activity such as exercising. This lowers blood pressure, cholesterol and sugar levels. Adults should be getting 2 hours and 30 minutes of exercise that is moderate in intensity, this includes; brisk walking or biking every week. Adolescents and children should get at least 1 hour of exercise every day. Exercising can also help control stress, improves sleep, boost mood and keeps weight in check.
Another way of lower your risk of heart disease is not smoking. If you currently smoke quitting will lower the risk for heart disease. Along with not smoking limiting the amount of alcohol consumed lowers your risk. Drinking too much alcohol can raise blood pressure. Men should have no more than two drinks per day and women should only have one.
Cardiovascular disease: conditions that involve narrowed/blocked blood vessels that can lead to health issues such as heart attack, hypertension, high blood pressure, or stroke.
- Symptoms: chest pain/tightness/discomfort, shortness of breath, pain or weakness in legs/arms, pain in neck, jaw, throat, or back, lightheadedness, dizziness, fainting, alterations in heartbeat, pale or blue skin, swelling in legs, abdomen or areas near the eyes, fatigue, dry or persistent cough, skin rashes or spots
- Risk factors: age, sex, family history, smoking, certain cancer treatments, poor diet, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, obesity, physical inactivity, stress, poor hygiene
- Prevention techniques: quit smoking, focus on lowering blood pressure/cholesterol if they’re high, exercise (at least 30 minutes a day is recommended), eat a low salt/saturated fat diet, maintain a healthy weight, reduce and manage stress, practice good hygiene
Hypertension: abnormally high blood pressure (higher than 130/80)
- Blood pressure: force exerted by the blood against the walls of the blood vessels (120/80 is normal)
- Pressure depends on work being done by the heart and the resistance of the blood vessels
- Symptoms: in most cases, there are no symptoms. However some people experience sweating, anxiety, sleeping problems, blushing, headaches, and nosebleeds.
- Risk factors: age, ethnicity, size & weight, alcohol & tobacco use, sex, existing health conditions, physical inactivity, salt-rich diet with processed/fatty foods, low potassium diet, certain diseases & medications, family history, poorly managed stress
- Treatments: regular physical exercise, stress reduction, healthy diet, some medications
- Hypertension-related atherosclerosis (narrowing of the blood vessels) can lead to heart failure, heart attacks, an aneurysm, kidney failure, stroke, amputation, or blindness from hypertensive retinopathies in the eye
Stroke: brain cells dying as a result of loss of oxygen from decreased blood flow to the brain
- Symptoms: sudden numbness or weakness or face, arm or leg (specifically on one side of body), sudden confusion, trouble speaking, or understanding, trouble seeing in one or both eyes, sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination, severe headache with no known cause
- Risk factors: diet and nutrition, physical activity, tobacco use and smoking, alcohol use, high blood pressure, AFib, high cholesterol, diabetes, circulation problems, age, gender, race and ethnicity, family history, previous stroke, FMD, PFO, TIA, risk for women greater than risk for men
- Prevention techniques: healthy diet, regular physical activity, quit smoking, low alcohol use, work to lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels if they’re high
- Impacts of stroke: weakness/numbness/stiffness, paralysis, seizures & epilepsy, trouble sleeping, vision problems, spasticity, incontinence, hemiparesis, foot drop, dysphagia, fatigue, depression, PBA, aphasia, memory loss, vascular dementia
Heart attack: the death of heart muscle due to the decrease of blood supply usually caused by a blockage of a coronary artery
- Treatments: drugs to dissolve/prevent blood clots, angioplasty or intracoronary stenting to open obstructed artery, medications that dilate blood vessels to increase blood flow
- Symptoms: Pain/tightness in chest, jaw pain, toothache, headache, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, general epigastric discomfort, sweating, heartburn/indigestion, arm pain (more commonly in left arm but can be either arm), upper back pain, neck & shoulder pain in women, abdominal pain, general malaise, or no symptoms at all (nicknamed “silent killer”)
- Risk factors: high blood cholesterol, high blood pressure, tobacco use, diabetes, males at greater risk than females, family history of heart disease.
Sources:
“Cognition.” National Stroke Association, www.stroke.org/we-can-help/survivors/stroke-recovery/post-stroke-conditions/cognition/.
“Heart Disease Prevention With Healthy Living Habits.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/healthy_living.htm.
“Heart Disease.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 22 Mar. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20353118.
“Heart Disease.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 22 Mar. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20353118.
“Heart Disease: Causes of a Heart Attack.” MedicineNet, www.medicinenet.com/heart_disease_pictures_slideshow_visual_guide/article.htm.
MacGill, Markus. “Hypertension: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments.” Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 21 Nov. 2018, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/150109.php.
“Preventing Heart Disease.” The Nutrition Source, 30 Jan. 2019, www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/disease-prevention/cardiovascular-disease/preventing-cvd/.
“What Is Cardiovascular Disease?” Www.heart.org, www.heart.org/en/health-topics/consumer-healthcare/what-is-cardiovascular-disease.