*There are three sections within this page:
1) Glossary Terms 2) Fish Illustrations 3) Web/Book Resources
Glossary Terms
- Abdomen – Fish’s belly (Between pelvic fins and anus of the lower side of the fish)
- Adhesive – Referring to eggs, those who stick to one another or a substrate after water hardening
- Adipose fin – small fin without rays located on the fish’s back between the dorsal fin and the tail
- Air or Swim Bladder – A balloon-like organ located in the gut of the fish that is either used for respiration or to control buoyancy
- Alevin – A newly hatched fish that still has its yolk-sac
- Anus – The external opening of the intestine, the vent
- Anal fin – one fin located on the bottom of the fish near the tail
- Bands – horizontal marks running lengthwise along the side of a fish
- Bars – Vertical markings on the side of the fish
- Barbel – thread-like sensory structures on a fish’s head by the mouth, “whiskers”
- Used for taste and smell
- Branchiostegal Rays – Bony rays supporting the membranes which close the gill cavity under the head
- Bristle – A stiff hair-like projection
- Carnivore – feeds on other fish or animals
- Caudal fin – tail fin
- Caudal Peduncle – body portion found between anal fin and beginning of the tail
- Caudal Spot – Spot on base of the caudal fin
- Chevron-shaped – Earliest developmental form of myomeres in larvae (angle formed by the epaxial and hypaxial portions of the myosepta)
- Chromatophore – A modified dermal cell that contains pigment that provide fish with color
- Chorion – The outermost membrane of a fish egg after water hardening
- Compressed – Flattened from side to side
- Copepod – small crustacean (zooplankton community)
- Ctenoid – Scales having small, needle-like projections on the posterior area
- Crustacean – Aquatic species that have paired antennae, jointed legs, and exterior skeleton
- Common food for most fish (crayfish, water flea, crabs, etc)
- Dorsal – top of fish or near the back
- Dorsum – The upper (dorsal) surface of the head or body
- Drainage – A group of lakes or streams within a basin (Ex: Lake Michigan)
- Epaxial – The portion of the body above the horizontal myoseptum
- Fin Base – Part of the fin attached to the body
- Finfold – Median folds that are a tough protective layer on the outside of their skin
- Forked – With the caudal fin, the rear edges are distinctly indented
- Fusiform – Cylindrical and tapering at both sides of the body
- Genus (plural: genera) – Taxonomic category including one species or a closely related group of species (sharing a common ancestor)
- Gills – Organs used for aquatic respiration
- Gill Cover – (Opercle or Operculum) Bones covering the gills
- Gonads – Sexual organs that produce eggs or sperm
- Habitat – Environment where a fish lives
- Herbivorous – Plant-eating fish
- Hypaxial – The portion of the body below the horizontal myoseptum
- Hypolimnion – In a thermally stratified lake, it is the bottom layer of the lake (depleted of oxygen by decaying water)
- Ichthyologist – A scientist who studies fish
- Inferior Mouth – Snout projecting beyond the lower jaw
- Invertebrates – Animals without backbones (Insects, crayfish, earthworms, leeches, etc)
- Invasive – Non-native species within a specific geographic location
- Juvenile – Young (small version of adult) fish that has developed complete fin ray development and finfold absorption to be sexual mature
- Keel – Shelf-like fleshy or bony ridge
- Larva (plural: larvae) – Newborn; developmental stage of fish before it becomes a juvenile
- Lateral – Side of fish
- Lateral Line – A series of pored scales along the side of a fish that contain organs which can be used to detect vibrations
- Lateral Scale-Count = Number of scales along lateral line
- Lateral Scales – Row of scales along the side (middle) of fish (gill cover to base of caudal fin)
- Littoral Zone – Spawning habitat (less than 15 feet deep) for freshwater fish that also holds the majority of aquatic plants in lakes
- Mandible – Lower Jaw
- Maxillary – Upper Jaw
- Melanophore – A dark brown or black pigment (cells containing melanin) (pepperlike dots)
- Mollusk – An invertebrate with a soft and smooth body (clams)
- Morphology – Form or structure of an organism
- Myomeres – Body segments
- Myoseptum – Thin partition of connective tissue which joins myomeres
- Nape – Upper surface of the body behind the head and before the dorsal fin
- Nares – Nostrils
- Native – An indigenous species
- Omnivore – A fish that eat both animal and plant matter
- Origin – Point where the fin begins
- Otolith – Ear bones (calcareous structures)
- Paired Fins – Pectoral and pelvic fins
- Pectoral Fins – paired fins on the side of the fish (behind the head/gills)
- Peduncle – Fleshy end of the body between the anal and caudal fins
- Pelvic Fins – paired fins below the pectoral fins on the bottom or ventral portion of the fish
- Perivitelline space – Fluid-filled space between the chorion and yolk material
- Piscivore – A predator fish that mainly eats other fish
- Pharyngeal Teeth – Bony tooth-like projections derived from the fifth gill arch
- Planktivore – A fish that feeds on plankton
- Plankton – Small plants (phytoplankton) and animals (zooplankton) mostly free-floating
- Plicae – Wrinkle-like folds found on the lips of some catostomids
- Pore – Tiny opening in the skin
- Postanal Length – Distance from the most posterior point of the anus to the most posterior point on the caudal fin or median finfold
- Postanal Myomeres – Number of whole myomeres posterior to an imaginary vertical line at the most posterior point of the anus
- Preanal Length – Distance from the most anterior point on the snout to the most posterior point on the anus
- Preanal Myomeres – Number of myomeres from the nape to an imaginary vertical line at the most posterior point of the anus
- Ray – Flexible, branched segmented fin. (Bony element that supports and spreads membranes)
- Redd – A nest-like depression made by either males or females during spawning
- Roe – Fish eggs
- Scales – small, flat plates covering the outer skin of fish
- Silt – small disturbed bottom particles (smaller than sand but bigger than clay)
- Snout – Portion of the head in front of eyes and above a mouth
- Spawning – The process of fish reproduction (Females lay eggs while males fertilize them)
- Spine – Hard, unsegmented and unbranched ray in fin (Spinous ray)
- Spiracle – An opening on the head above and behind the eye that is a canal leading to gill chambers in bony fish
- Spot – Circular color marks
- Standard Length – Length of the fish from the mouth to the end of the vertebral column (before the tail (caudal fin))
- Stripe – Horizontal band of color
- Subspecies – Geographically diagnosable population of a species
- Substrate – Bottom composition of water bodies (lake, river, streams, etc)
- Subterminal – Mouth opens below foremost point of head (Mouth Position)
- Superior Mouth – Condition when the lower jaw extends upward and the mouth opens dorsally
- Tail – Portion of the body posterior to the anus (Larvae)
- Teleost – Large group containing most of the bony fish
- Thermocline – The middle layer of a stratified lake which is oxygen-rich and characterized by its sharp drops in water temperature
- Terminal Mouth – Condition when the lower and upper jaws are equal in length and the mouth opens terminally
- Territorial – Defending of a particular area
- Total Length – Length of fish from the mouth to the tail
- Tributary – Stream that feeds into another water body
- Turbid – Water cloudy by suspended solids or plant matter (limits visibility and sunlight penetration)
- Urostyle – Final vertebral segment usually modified for caudal fin support
- Ventral – Underside of fish
- Vertebrate – An animal with a backbone
- Water Hardening – Process of membrane delamination and fluid formation which forms the perivitelline space
- Yolk – Part of the egg that contains food for developing fish
- Yolk Sac – Ventral extension of the gut containing yolk
- Yolk Sac Larvae – Phase of development from hatching to complete absorption of yolk
- Zooplankton – tiny animals that float or swim weakly that are a common food for small fish
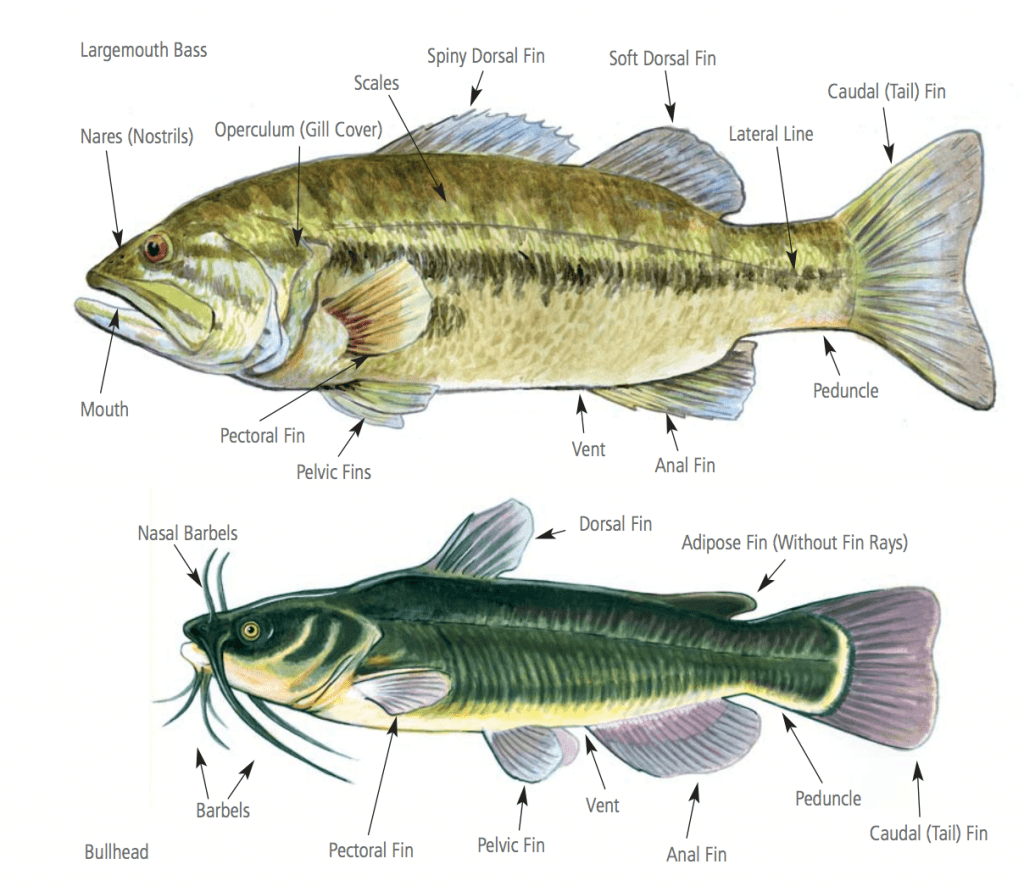
Illustrations of Fish Morphology
*Click on the visual to better understand and identify physical characteristics of fish.*
Fish Anatomy Illustrations
*Click on visual to learn more about their body forms, coloration patterns, fin types, and mouth morphology.*
Glossary Book Resources
- Auer, N. A. (ed.). 1982. Identification of larval fishes of the Great Lakes basin with emphasis on the Lake Michigan drainage. Great Lakes Fishery Commission, Ann Arbor, MI 48105. Special Pub. 82-3:744 pp.
- Bosanko, Dave. 2007. Fish of Wisconsin – Field Guide. Adventure Publications, Inc. Cambridge, MN. Print
- Burr, B & Page, L. 2011. Peterson – Field Guide to Freshwater Fishes. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. New York, NY. Print.
- Becker, George. Fishes of Wisconsin. University of Wisconsin, Press. Madison, WI. 1983. Print.