Lauren Butler
Air Pollution Statistics and History
As America grows, our air quality improves. Through statistics and documented history, we can see that concentrations of air pollutants have dropped significantly, death rates due to air pollution are on the decline, and our perception of air pollution has changed.
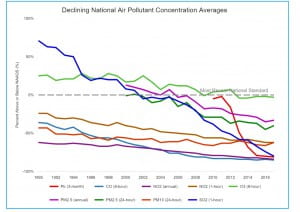
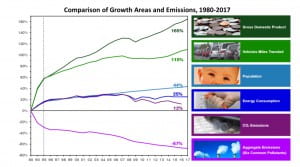
Concentrations of air pollutants have dropped significantly. Since 1990 Carbon Monoxide, Lead, Nitrogen Dioxide, ozone, particulate matter at 10 and 2.5 Microns, and Sulfur Dioxide levels have dropped. Despite our population growth, air pollutant concentration continues to decline. It’s very unlikely to see a future without air pollutants, but if the trend continues, we will see cleaner air.
Carbon Monoxide (down 77%), Lead (down 80%), Nitrogen Dioxide (Annual, down 56%; 1 Hour, down 50%), Ozone (down 22%), Particulate Matter 10 Microns (down 34%), Particulate Matter 2.5 Microns (Annual, down 41%; 24 Hour, down 40%), Sulfur Dioxide (down 88%)
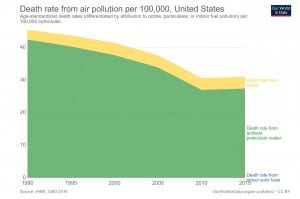
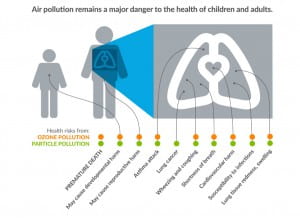
Even though the concentration of air pollutants is at a historical low, there are still health risks. Death rates from air pollution have declined over the past few decades. It’s difficult to directly attribute the cause of death to air pollution. Death due to air pollution is defined as someone that dies prematurely than would be expected in the absence of air pollution. Air pollution is associated with a number of health problems including heart attacks, asthma attacks, and bronchitis. Air pollution bothers those with heart or lung diseases (like asthma), older adults, and babies and children.
Over the past few decades our perception of air pollution has changed. In 1955 the first United States federal legislation that had to do with research of air pollution was enacted, the Air Pollution Control Act. The first legislation to control air pollution was the Clean Air Act, which started in 1963. This act established a program that researched techniques for monitoring and controlling air pollution. In 1960 there were six states with air pollution programs. In 1965 the Motor Vehicle Air Pollution Control Act was amended to set required standards for controlling the emission of pollutants from certain vehicles. The second amendment was in 1967; the Air Quality Act enabled the government to increase investigations of interstate air pollution transport and expanded studies of air pollution emission inventories, ambient monitoring techniques, and control techniques. By 1970 all fifty states had air pollution programs, amendments for stationary pollution sources and mobile sources, and the EPA was established. More amendments were made in 1990 for problems with acid rain, ozone depletion, and toxic air pollution. Since the beginning of the United States’ action towards clean air, we can see the growth. At the start, we believed that air pollution was a problem brought on by vehicles. Now we understand that air pollution is caused by burning fossil fuels, agricultural activity, factories and industries, mining, and indoor air pollution
Sources
https://www.ourworldindata.org/air-pollution/
https://www.epa.gov/air-trends
https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-inventories/air-pollutant-emissions-trends-data
https://gispub.epa.gov/air/trendsreport/2018/#growth_w_cleaner_air
https://www.cdc.gov/air/particulate_matter.html
https://www.epa.gov/pmcourse/what-particle-pollution
https://www.epa.gov/laws-regulations/summary-clean-air-act https://www.epa.gov/clean-air-act-overview/1990-clean-air-act-amendment-summary
https://www.conserve-energy-future.com/causes-effects-solutions-of-air-pollution.php